mirror of https://github.com/libp2p/go-libp2p.git
70 changed files with 226 additions and 6262 deletions
@ -1 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package backpressure_tests |
|||
@ -1,373 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package backpressure_tests |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
crand "crypto/rand" |
|||
"io" |
|||
"math/rand" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
netutil "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/swarmnet/util" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = eventlog.Logger("backpressure") |
|||
|
|||
// TestBackpressureStreamHandler tests whether mux handler
|
|||
// ratelimiting works. Meaning, since the handler is sequential
|
|||
// it should block senders.
|
|||
//
|
|||
// Important note: spdystream (which peerstream uses) has a set
|
|||
// of n workers (n=spdsystream.FRAME_WORKERS) which handle new
|
|||
// frames, including those starting new streams. So all of them
|
|||
// can be in the handler at one time. Also, the sending side
|
|||
// does not rate limit unless we call stream.Wait()
|
|||
//
|
|||
//
|
|||
// Note: right now, this happens muxer-wide. the muxer should
|
|||
// learn to flow control, so handlers cant block each other.
|
|||
func TestBackpressureStreamHandler(t *testing.T) { |
|||
t.Skip(`Sadly, as cool as this test is, it doesn't work |
|||
Because spdystream doesnt handle stream open backpressure |
|||
well IMO. I'll see about rewriting that part when it becomes |
|||
a problem. |
|||
`) |
|||
|
|||
// a number of concurrent request handlers
|
|||
limit := 10 |
|||
|
|||
// our way to signal that we're done with 1 request
|
|||
requestHandled := make(chan struct{}) |
|||
|
|||
// handler rate limiting
|
|||
receiverRatelimit := make(chan struct{}, limit) |
|||
for i := 0; i < limit; i++ { |
|||
receiverRatelimit <- struct{}{} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// sender counter of successfully opened streams
|
|||
senderOpened := make(chan struct{}, limit*100) |
|||
|
|||
// sender signals it's done (errored out)
|
|||
senderDone := make(chan struct{}) |
|||
|
|||
// the receiver handles requests with some rate limiting
|
|||
receiver := func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
log.Debug("receiver received a stream") |
|||
|
|||
<-receiverRatelimit // acquire
|
|||
go func() { |
|||
// our request handler. can do stuff here. we
|
|||
// simulate something taking time by waiting
|
|||
// on requestHandled
|
|||
log.Error("request worker handling...") |
|||
<-requestHandled |
|||
log.Error("request worker done!") |
|||
receiverRatelimit <- struct{}{} // release
|
|||
}() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// the sender opens streams as fast as possible
|
|||
sender := func(net inet.Network, remote peer.ID) { |
|||
var s inet.Stream |
|||
var err error |
|||
defer func() { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
log.Debug("sender error. exiting.") |
|||
senderDone <- struct{}{} |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
for { |
|||
s, err = net.NewStream(inet.ProtocolTesting, remote) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
_ = s |
|||
// if err = s.SwarmStream().Stream().Wait(); err != nil {
|
|||
// return
|
|||
// }
|
|||
|
|||
// "count" another successfully opened stream
|
|||
// (large buffer so shouldn't block in normal operation)
|
|||
log.Debug("sender opened another stream!") |
|||
senderOpened <- struct{}{} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// count our senderOpened events
|
|||
countStreamsOpenedBySender := func(min int) int { |
|||
opened := 0 |
|||
for opened < min { |
|||
log.Debugf("countStreamsOpenedBySender got %d (min %d)", opened, min) |
|||
select { |
|||
case <-senderOpened: |
|||
opened++ |
|||
case <-time.After(10 * time.Millisecond): |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return opened |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// count our received events
|
|||
// waitForNReceivedStreams := func(n int) {
|
|||
// for n > 0 {
|
|||
// log.Debugf("waiting for %d received streams...", n)
|
|||
// select {
|
|||
// case <-receiverRatelimit:
|
|||
// n--
|
|||
// }
|
|||
// }
|
|||
// }
|
|||
|
|||
testStreamsOpened := func(expected int) { |
|||
log.Debugf("testing rate limited to %d streams", expected) |
|||
if n := countStreamsOpenedBySender(expected); n != expected { |
|||
t.Fatalf("rate limiting did not work :( -- %d != %d", expected, n) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok that's enough setup. let's do it!
|
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
n1 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n2 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
// setup receiver handler
|
|||
n1.SetHandler(inet.ProtocolTesting, receiver) |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("dialing %s", n2.ListenAddresses()) |
|||
if err := n1.DialPeer(ctx, n2.LocalPeer()); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// launch sender!
|
|||
go sender(n2, n1.LocalPeer()) |
|||
|
|||
// ok, what do we expect to happen? the receiver should
|
|||
// receive 10 requests and stop receiving, blocking the sender.
|
|||
// we can test this by counting 10x senderOpened requests
|
|||
|
|||
<-senderOpened // wait for the sender to successfully open some.
|
|||
testStreamsOpened(limit - 1) |
|||
|
|||
// let's "handle" 3 requests.
|
|||
<-requestHandled |
|||
<-requestHandled |
|||
<-requestHandled |
|||
// the sender should've now been able to open exactly 3 more.
|
|||
|
|||
testStreamsOpened(3) |
|||
|
|||
// shouldn't have opened anything more
|
|||
testStreamsOpened(0) |
|||
|
|||
// let's "handle" 100 requests in batches of 5
|
|||
for i := 0; i < 20; i++ { |
|||
<-requestHandled |
|||
<-requestHandled |
|||
<-requestHandled |
|||
<-requestHandled |
|||
<-requestHandled |
|||
testStreamsOpened(5) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// success!
|
|||
|
|||
// now for the sugar on top: let's tear down the receiver. it should
|
|||
// exit the sender.
|
|||
n1.Close() |
|||
|
|||
// shouldn't have opened anything more
|
|||
testStreamsOpened(0) |
|||
|
|||
select { |
|||
case <-time.After(100 * time.Millisecond): |
|||
t.Error("receiver shutdown failed to exit sender") |
|||
case <-senderDone: |
|||
log.Info("handler backpressure works!") |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// TestStBackpressureStreamWrite tests whether streams see proper
|
|||
// backpressure when writing data over the network streams.
|
|||
func TestStBackpressureStreamWrite(t *testing.T) { |
|||
|
|||
// senderWrote signals that the sender wrote bytes to remote.
|
|||
// the value is the count of bytes written.
|
|||
senderWrote := make(chan int, 10000) |
|||
|
|||
// sender signals it's done (errored out)
|
|||
senderDone := make(chan struct{}) |
|||
|
|||
// writeStats lets us listen to all the writes and return
|
|||
// how many happened and how much was written
|
|||
writeStats := func() (int, int) { |
|||
writes := 0 |
|||
bytes := 0 |
|||
for { |
|||
select { |
|||
case n := <-senderWrote: |
|||
writes++ |
|||
bytes = bytes + n |
|||
default: |
|||
log.Debugf("stats: sender wrote %d bytes, %d writes", bytes, writes) |
|||
return bytes, writes |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// sender attempts to write as fast as possible, signaling on the
|
|||
// completion of every write. This makes it possible to see how
|
|||
// fast it's actually writing. We pair this with a receiver
|
|||
// that waits for a signal to read.
|
|||
sender := func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
defer func() { |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
senderDone <- struct{}{} |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
// ready a buffer of random data
|
|||
buf := make([]byte, 65536) |
|||
crand.Read(buf) |
|||
|
|||
for { |
|||
// send a randomly sized subchunk
|
|||
from := rand.Intn(len(buf) / 2) |
|||
to := rand.Intn(len(buf) / 2) |
|||
sendbuf := buf[from : from+to] |
|||
|
|||
n, err := s.Write(sendbuf) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
log.Debug("sender error. exiting:", err) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("sender wrote %d bytes", n) |
|||
senderWrote <- n |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// receive a number of bytes from a stream.
|
|||
// returns the number of bytes written.
|
|||
receive := func(s inet.Stream, expect int) { |
|||
log.Debugf("receiver to read %d bytes", expect) |
|||
rbuf := make([]byte, expect) |
|||
n, err := io.ReadFull(s, rbuf) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Error("read failed:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
if expect != n { |
|||
t.Error("read len differs: %d != %d", expect, n) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok let's do it!
|
|||
|
|||
// setup the networks
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
n1 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n2 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n1, n2) |
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n2, n1) |
|||
|
|||
// setup sender handler on 1
|
|||
n1.SetHandler(inet.ProtocolTesting, sender) |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("dialing %s", n2.ListenAddresses()) |
|||
if err := n1.DialPeer(ctx, n2.LocalPeer()); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// open a stream, from 2->1, this is our reader
|
|||
s, err := n2.NewStream(inet.ProtocolTesting, n1.LocalPeer()) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// let's make sure r/w works.
|
|||
testSenderWrote := func(bytesE int) { |
|||
bytesA, writesA := writeStats() |
|||
if bytesA != bytesE { |
|||
t.Errorf("numbers failed: %d =?= %d bytes, via %d writes", bytesA, bytesE, writesA) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// 500ms rounds of lockstep write + drain
|
|||
roundsStart := time.Now() |
|||
roundsTotal := 0 |
|||
for roundsTotal < (2 << 20) { |
|||
// let the sender fill its buffers, it will stop sending.
|
|||
<-time.After(300 * time.Millisecond) |
|||
b, _ := writeStats() |
|||
testSenderWrote(0) |
|||
testSenderWrote(0) |
|||
|
|||
// drain it all, wait again
|
|||
receive(s, b) |
|||
roundsTotal = roundsTotal + b |
|||
} |
|||
roundsTime := time.Now().Sub(roundsStart) |
|||
|
|||
// now read continously, while we measure stats.
|
|||
stop := make(chan struct{}) |
|||
contStart := time.Now() |
|||
|
|||
go func() { |
|||
for { |
|||
select { |
|||
case <-stop: |
|||
return |
|||
default: |
|||
receive(s, 2<<15) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
contTotal := 0 |
|||
for contTotal < (2 << 20) { |
|||
n := <-senderWrote |
|||
contTotal += n |
|||
} |
|||
stop <- struct{}{} |
|||
contTime := time.Now().Sub(contStart) |
|||
|
|||
// now compare! continuous should've been faster AND larger
|
|||
if roundsTime < contTime { |
|||
t.Error("continuous should have been faster") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if roundsTotal < contTotal { |
|||
t.Error("continuous should have been larger, too!") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// and a couple rounds more for good measure ;)
|
|||
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ { |
|||
// let the sender fill its buffers, it will stop sending.
|
|||
<-time.After(300 * time.Millisecond) |
|||
b, _ := writeStats() |
|||
testSenderWrote(0) |
|||
testSenderWrote(0) |
|||
|
|||
// drain it all, wait again
|
|||
receive(s, b) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// this doesn't work :(:
|
|||
// // now for the sugar on top: let's tear down the receiver. it should
|
|||
// // exit the sender.
|
|||
// n1.Close()
|
|||
// testSenderWrote(0)
|
|||
// testSenderWrote(0)
|
|||
// select {
|
|||
// case <-time.After(2 * time.Second):
|
|||
// t.Error("receiver shutdown failed to exit sender")
|
|||
// case <-senderDone:
|
|||
// log.Info("handler backpressure works!")
|
|||
// }
|
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,52 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package conn |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
|
|||
handshake "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/handshake" |
|||
hspb "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/handshake/pb" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ggprotoio "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/gogoprotobuf/io" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// Handshake1 exchanges local and remote versions and compares them
|
|||
// closes remote and returns an error in case of major difference
|
|||
func Handshake1(ctx context.Context, c Conn) error { |
|||
rpeer := c.RemotePeer() |
|||
lpeer := c.LocalPeer() |
|||
|
|||
// setup up protobuf io
|
|||
maxSize := 4096 |
|||
r := ggprotoio.NewDelimitedReader(c, maxSize) |
|||
w := ggprotoio.NewDelimitedWriter(c) |
|||
localH := handshake.Handshake1Msg() |
|||
remoteH := new(hspb.Handshake1) |
|||
|
|||
// send the outgoing handshake message
|
|||
if err := w.WriteMsg(localH); err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
log.Debugf("%p sent my version (%s) to %s", c, localH, rpeer) |
|||
log.Event(ctx, "handshake1Sent", lpeer) |
|||
|
|||
select { |
|||
case <-ctx.Done(): |
|||
return ctx.Err() |
|||
default: |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if err := r.ReadMsg(remoteH); err != nil { |
|||
return fmt.Errorf("could not receive remote version: %q", err) |
|||
} |
|||
log.Debugf("%p received remote version (%s) from %s", c, remoteH, rpeer) |
|||
log.Event(ctx, "handshake1Received", lpeer) |
|||
|
|||
if err := handshake.Handshake1Compatible(localH, remoteH); err != nil { |
|||
log.Infof("%s (%s) incompatible version with %s (%s)", lpeer, localH, rpeer, remoteH) |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s version handshake compatible %s", lpeer, rpeer) |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@ |
|||
# IFPS Handshake |
|||
|
|||
The IPFS Protocol Handshake is divided into three sequential steps |
|||
|
|||
1. Version Handshake (`Hanshake1`) |
|||
2. Secure Channel (`NewSecureConn`) |
|||
3. Services (`Handshake3`) |
|||
|
|||
Currently these parts currently happen sequentially (costing an awful 5 RTT), |
|||
but can be optimized to 2 RTT. |
|||
|
|||
### Version Handshake |
|||
|
|||
The Version Handshake ensures that nodes speaking to each other can interoperate. |
|||
They send each other protocol versions and ensure there is a match on the major |
|||
version (semver). |
|||
|
|||
### Secure Channel |
|||
|
|||
The second part exchanges keys and establishes a secure comm channel. This |
|||
follows ECDHE TLS, but *isn't* TLS. (why will be written up elsewhere). |
|||
|
|||
### Services |
|||
|
|||
The Services portion sends any additional information on nodes needed |
|||
by the nodes, e.g. Listen Address (the received address could be a Dial addr), |
|||
and later on can include Service listing (dht, exchange, ipns, etc). |
|||
@ -1,34 +0,0 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
package handshake implements the ipfs handshake protocol |
|||
|
|||
IPFS Handshake |
|||
|
|||
The IPFS Protocol Handshake is divided into three sequential steps |
|||
|
|||
1. Version Handshake (`Hanshake1`) |
|||
|
|||
2. Secure Channel (`NewSecureConn`) |
|||
|
|||
3. Services (`Handshake3`) |
|||
|
|||
Currently these parts currently happen sequentially (costing an awful 5 RTT), |
|||
but can be optimized to 2 RTT. |
|||
|
|||
Version Handshake |
|||
|
|||
The Version Handshake ensures that nodes speaking to each other can interoperate. |
|||
They send each other protocol versions and ensure there is a match on the major |
|||
version (semver). |
|||
|
|||
Secure Channel |
|||
|
|||
The second part exchanges keys and establishes a secure comm channel. This |
|||
follows ECDHE TLS, but *isn't* TLS. (why will be written up elsewhere). |
|||
|
|||
Services |
|||
|
|||
The Services portion sends any additional information on nodes needed |
|||
by the nodes, e.g. Listen Address (the received address could be a Dial addr), |
|||
and later on can include Service listing (dht, exchange, ipns, etc). |
|||
*/ |
|||
package handshake |
|||
@ -1,68 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package handshake |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"errors" |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
|
|||
config "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/config" |
|||
pb "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/handshake/pb" |
|||
u "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util" |
|||
|
|||
semver "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/coreos/go-semver/semver" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = u.Logger("handshake") |
|||
|
|||
// IpfsVersion holds the current protocol version for a client running this code
|
|||
var IpfsVersion *semver.Version |
|||
var ClientVersion = "go-ipfs/" + config.CurrentVersionNumber |
|||
|
|||
func init() { |
|||
var err error |
|||
IpfsVersion, err = semver.NewVersion("0.0.1") |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
panic(fmt.Errorf("invalid protocol version: %v", err)) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Handshake1Msg returns the current protocol version as a protobuf message
|
|||
func Handshake1Msg() *pb.Handshake1 { |
|||
return NewHandshake1(IpfsVersion.String(), ClientVersion) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ErrVersionMismatch is returned when two clients don't share a protocol version
|
|||
var ErrVersionMismatch = errors.New("protocol missmatch") |
|||
|
|||
// Handshake1Compatible checks whether two versions are compatible
|
|||
// returns nil if they are fine
|
|||
func Handshake1Compatible(handshakeA, handshakeB *pb.Handshake1) error { |
|||
a, err := semver.NewVersion(*handshakeA.ProtocolVersion) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
b, err := semver.NewVersion(*handshakeB.ProtocolVersion) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if a.Major != b.Major { |
|||
return ErrVersionMismatch |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NewHandshake1 creates a new Handshake1 from the two strings
|
|||
func NewHandshake1(protoVer, agentVer string) *pb.Handshake1 { |
|||
if protoVer == "" { |
|||
protoVer = IpfsVersion.String() |
|||
} |
|||
if agentVer == "" { |
|||
agentVer = ClientVersion |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return &pb.Handshake1{ |
|||
ProtocolVersion: &protoVer, |
|||
AgentVersion: &agentVer, |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package handshake |
|||
|
|||
import "testing" |
|||
|
|||
func TestH1Compatible(t *testing.T) { |
|||
tcases := []struct { |
|||
a, b string |
|||
expected error |
|||
}{ |
|||
{"0.0.0", "0.0.0", nil}, |
|||
{"1.0.0", "1.1.0", nil}, |
|||
{"1.0.0", "1.0.1", nil}, |
|||
{"0.0.0", "1.0.0", ErrVersionMismatch}, |
|||
{"1.0.0", "0.0.0", ErrVersionMismatch}, |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for i, tcase := range tcases { |
|||
|
|||
if Handshake1Compatible(NewHandshake1(tcase.a, ""), NewHandshake1(tcase.b, "")) != tcase.expected { |
|||
t.Fatalf("case[%d] failed", i) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@ |
|||
|
|||
PB = $(wildcard *.proto) |
|||
GO = $(PB:.proto=.pb.go) |
|||
|
|||
all: $(GO) |
|||
|
|||
%.pb.go: %.proto |
|||
protoc --gogo_out=. --proto_path=../../../../../../:/usr/local/opt/protobuf/include:. $< |
|||
|
|||
clean: |
|||
rm *.pb.go |
|||
@ -1,113 +0,0 @@ |
|||
// Code generated by protoc-gen-gogo.
|
|||
// source: handshake.proto
|
|||
// DO NOT EDIT!
|
|||
|
|||
/* |
|||
Package handshake_pb is a generated protocol buffer package. |
|||
|
|||
It is generated from these files: |
|||
handshake.proto |
|||
|
|||
It has these top-level messages: |
|||
Handshake1 |
|||
Handshake3 |
|||
*/ |
|||
package handshake_pb |
|||
|
|||
import proto "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/gogoprotobuf/proto" |
|||
import json "encoding/json" |
|||
import math "math" |
|||
|
|||
// Reference proto, json, and math imports to suppress error if they are not otherwise used.
|
|||
var _ = proto.Marshal |
|||
var _ = &json.SyntaxError{} |
|||
var _ = math.Inf |
|||
|
|||
// Handshake1 is delivered _before_ the secure channel is initialized
|
|||
type Handshake1 struct { |
|||
// protocolVersion determines compatibility between peers
|
|||
ProtocolVersion *string `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=protocolVersion" json:"protocolVersion,omitempty"` |
|||
// agentVersion is like a UserAgent string in browsers, or client version in bittorrent
|
|||
// includes the client name and client. e.g. "go-ipfs/0.1.0"
|
|||
AgentVersion *string `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=agentVersion" json:"agentVersion,omitempty"` |
|||
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"` |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (m *Handshake1) Reset() { *m = Handshake1{} } |
|||
func (m *Handshake1) String() string { return proto.CompactTextString(m) } |
|||
func (*Handshake1) ProtoMessage() {} |
|||
|
|||
func (m *Handshake1) GetProtocolVersion() string { |
|||
if m != nil && m.ProtocolVersion != nil { |
|||
return *m.ProtocolVersion |
|||
} |
|||
return "" |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (m *Handshake1) GetAgentVersion() string { |
|||
if m != nil && m.AgentVersion != nil { |
|||
return *m.AgentVersion |
|||
} |
|||
return "" |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Handshake3 is delivered _after_ the secure channel is initialized
|
|||
type Handshake3 struct { |
|||
// can include all the values in handshake1, for protocol version, etc.
|
|||
H1 *Handshake1 `protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=h1" json:"h1,omitempty"` |
|||
// publicKey is this node's public key (which also gives its node.ID)
|
|||
// - may not need to be sent, as secure channel implies it has been sent.
|
|||
// - then again, if we change / disable secure channel, may still want it.
|
|||
PublicKey []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=publicKey" json:"publicKey,omitempty"` |
|||
// listenAddrs are the multiaddrs the sender node listens for open connections on
|
|||
ListenAddrs [][]byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=listenAddrs" json:"listenAddrs,omitempty"` |
|||
// protocols are the services this node is running
|
|||
Protocols []string `protobuf:"bytes,3,rep,name=protocols" json:"protocols,omitempty"` |
|||
// oservedAddr is the multiaddr of the remote endpoint that the sender node perceives
|
|||
// this is useful information to convey to the other side, as it helps the remote endpoint
|
|||
// determine whether its connection to the local peer goes through NAT.
|
|||
ObservedAddr []byte `protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=observedAddr" json:"observedAddr,omitempty"` |
|||
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"` |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (m *Handshake3) Reset() { *m = Handshake3{} } |
|||
func (m *Handshake3) String() string { return proto.CompactTextString(m) } |
|||
func (*Handshake3) ProtoMessage() {} |
|||
|
|||
func (m *Handshake3) GetH1() *Handshake1 { |
|||
if m != nil { |
|||
return m.H1 |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (m *Handshake3) GetPublicKey() []byte { |
|||
if m != nil { |
|||
return m.PublicKey |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (m *Handshake3) GetListenAddrs() [][]byte { |
|||
if m != nil { |
|||
return m.ListenAddrs |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (m *Handshake3) GetProtocols() []string { |
|||
if m != nil { |
|||
return m.Protocols |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (m *Handshake3) GetObservedAddr() []byte { |
|||
if m != nil { |
|||
return m.ObservedAddr |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func init() { |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package handshake.pb; |
|||
|
|||
//import "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/net/mux/mux.proto"; |
|||
|
|||
// Handshake1 is delivered _before_ the secure channel is initialized |
|||
message Handshake1 { |
|||
// protocolVersion determines compatibility between peers |
|||
optional string protocolVersion = 1; // semver |
|||
|
|||
// agentVersion is like a UserAgent string in browsers, or client version in bittorrent |
|||
// includes the client name and client. e.g. "go-ipfs/0.1.0" |
|||
optional string agentVersion = 2; // semver |
|||
|
|||
// we'll have more fields here later. |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Handshake3 is delivered _after_ the secure channel is initialized |
|||
message Handshake3 { |
|||
|
|||
// can include all the values in handshake1, for protocol version, etc. |
|||
optional Handshake1 h1 = 5; |
|||
|
|||
// publicKey is this node's public key (which also gives its node.ID) |
|||
// - may not need to be sent, as secure channel implies it has been sent. |
|||
// - then again, if we change / disable secure channel, may still want it. |
|||
optional bytes publicKey = 1; |
|||
|
|||
// listenAddrs are the multiaddrs the sender node listens for open connections on |
|||
repeated bytes listenAddrs = 2; |
|||
|
|||
// protocols are the services this node is running |
|||
repeated string protocols = 3; |
|||
|
|||
// oservedAddr is the multiaddr of the remote endpoint that the sender node perceives |
|||
// this is useful information to convey to the other side, as it helps the remote endpoint |
|||
// determine whether its connection to the local peer goes through NAT. |
|||
optional bytes observedAddr = 4; |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,187 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package identify |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"sync" |
|||
|
|||
ggio "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/gogoprotobuf/io" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
handshake "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/handshake" |
|||
pb "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/handshake/pb" |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = eventlog.Logger("net/identify") |
|||
|
|||
// ProtocolIdentify is the ProtocolID of the Identify Service.
|
|||
const ProtocolIdentify inet.ProtocolID = "/ipfs/identify" |
|||
|
|||
// IDService is a structure that implements ProtocolIdentify.
|
|||
// It is a trivial service that gives the other peer some
|
|||
// useful information about the local peer. A sort of hello.
|
|||
//
|
|||
// The IDService sends:
|
|||
// * Our IPFS Protocol Version
|
|||
// * Our IPFS Agent Version
|
|||
// * Our public Listen Addresses
|
|||
type IDService struct { |
|||
Network inet.Network |
|||
|
|||
// connections undergoing identification
|
|||
// for wait purposes
|
|||
currid map[inet.Conn]chan struct{} |
|||
currmu sync.RWMutex |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func NewIDService(n inet.Network) *IDService { |
|||
s := &IDService{ |
|||
Network: n, |
|||
currid: make(map[inet.Conn]chan struct{}), |
|||
} |
|||
n.SetHandler(ProtocolIdentify, s.RequestHandler) |
|||
return s |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (ids *IDService) IdentifyConn(c inet.Conn) { |
|||
ids.currmu.Lock() |
|||
if wait, found := ids.currid[c]; found { |
|||
ids.currmu.Unlock() |
|||
log.Debugf("IdentifyConn called twice on: %s", c) |
|||
<-wait // already identifying it. wait for it.
|
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
ids.currid[c] = make(chan struct{}) |
|||
ids.currmu.Unlock() |
|||
|
|||
s, err := c.NewStreamWithProtocol(ProtocolIdentify) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
log.Error("network: unable to open initial stream for %s", ProtocolIdentify) |
|||
log.Event(ids.Network.CtxGroup().Context(), "IdentifyOpenFailed", c.RemotePeer()) |
|||
} else { |
|||
|
|||
// ok give the response to our handler.
|
|||
ids.ResponseHandler(s) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
ids.currmu.Lock() |
|||
ch, found := ids.currid[c] |
|||
delete(ids.currid, c) |
|||
ids.currmu.Unlock() |
|||
|
|||
if !found { |
|||
log.Errorf("IdentifyConn failed to find channel (programmer error) for %s", c) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
close(ch) // release everyone waiting.
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (ids *IDService) RequestHandler(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
defer s.Close() |
|||
c := s.Conn() |
|||
|
|||
w := ggio.NewDelimitedWriter(s) |
|||
mes := pb.Handshake3{} |
|||
ids.populateMessage(&mes, s.Conn()) |
|||
w.WriteMsg(&mes) |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s sent message to %s %s", ProtocolIdentify, |
|||
c.RemotePeer(), c.RemoteMultiaddr()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (ids *IDService) ResponseHandler(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
defer s.Close() |
|||
c := s.Conn() |
|||
|
|||
r := ggio.NewDelimitedReader(s, 2048) |
|||
mes := pb.Handshake3{} |
|||
if err := r.ReadMsg(&mes); err != nil { |
|||
log.Errorf("%s error receiving message from %s %s", ProtocolIdentify, |
|||
c.RemotePeer(), c.RemoteMultiaddr()) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
ids.consumeMessage(&mes, c) |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s received message from %s %s", ProtocolIdentify, |
|||
c.RemotePeer(), c.RemoteMultiaddr()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (ids *IDService) populateMessage(mes *pb.Handshake3, c inet.Conn) { |
|||
|
|||
// set protocols this node is currently handling
|
|||
protos := ids.Network.Protocols() |
|||
mes.Protocols = make([]string, len(protos)) |
|||
for i, p := range protos { |
|||
mes.Protocols[i] = string(p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// observed address so other side is informed of their
|
|||
// "public" address, at least in relation to us.
|
|||
mes.ObservedAddr = c.RemoteMultiaddr().Bytes() |
|||
|
|||
// set listen addrs
|
|||
laddrs, err := ids.Network.InterfaceListenAddresses() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
log.Error(err) |
|||
} else { |
|||
mes.ListenAddrs = make([][]byte, len(laddrs)) |
|||
for i, addr := range laddrs { |
|||
mes.ListenAddrs[i] = addr.Bytes() |
|||
} |
|||
log.Debugf("%s sent listen addrs to %s: %s", c.LocalPeer(), c.RemotePeer(), laddrs) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// set protocol versions
|
|||
mes.H1 = handshake.NewHandshake1("", "") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (ids *IDService) consumeMessage(mes *pb.Handshake3, c inet.Conn) { |
|||
p := c.RemotePeer() |
|||
|
|||
// mes.Protocols
|
|||
// mes.ObservedAddr
|
|||
|
|||
// mes.ListenAddrs
|
|||
laddrs := mes.GetListenAddrs() |
|||
lmaddrs := make([]ma.Multiaddr, 0, len(laddrs)) |
|||
for _, addr := range laddrs { |
|||
maddr, err := ma.NewMultiaddrBytes(addr) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
log.Errorf("%s failed to parse multiaddr from %s %s", ProtocolIdentify, p, |
|||
c.RemoteMultiaddr()) |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
lmaddrs = append(lmaddrs, maddr) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// update our peerstore with the addresses.
|
|||
ids.Network.Peerstore().AddAddresses(p, lmaddrs) |
|||
log.Debugf("%s received listen addrs for %s: %s", c.LocalPeer(), c.RemotePeer(), lmaddrs) |
|||
|
|||
// get protocol versions
|
|||
pv := *mes.H1.ProtocolVersion |
|||
av := *mes.H1.AgentVersion |
|||
ids.Network.Peerstore().Put(p, "ProtocolVersion", pv) |
|||
ids.Network.Peerstore().Put(p, "AgentVersion", av) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// IdentifyWait returns a channel which will be closed once
|
|||
// "ProtocolIdentify" (handshake3) finishes on given conn.
|
|||
// This happens async so the connection can start to be used
|
|||
// even if handshake3 knowledge is not necesary.
|
|||
// Users **MUST** call IdentifyWait _after_ IdentifyConn
|
|||
func (ids *IDService) IdentifyWait(c inet.Conn) <-chan struct{} { |
|||
ids.currmu.Lock() |
|||
ch, found := ids.currid[c] |
|||
ids.currmu.Unlock() |
|||
if found { |
|||
return ch |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// if not found, it means we are already done identifying it, or
|
|||
// haven't even started. either way, return a new channel closed.
|
|||
ch = make(chan struct{}) |
|||
close(ch) |
|||
return ch |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,111 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package identify_test |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"testing" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
handshake "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/handshake" |
|||
netutil "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/swarmnet/util" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
func subtestIDService(t *testing.T, postDialWait time.Duration) { |
|||
|
|||
// the generated networks should have the id service wired in.
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
n1 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n2 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
n1p := n1.LocalPeer() |
|||
n2p := n2.LocalPeer() |
|||
|
|||
testKnowsAddrs(t, n1, n2p, []ma.Multiaddr{}) // nothing
|
|||
testKnowsAddrs(t, n2, n1p, []ma.Multiaddr{}) // nothing
|
|||
|
|||
// have n2 tell n1, so we can dial...
|
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n2, n1) |
|||
|
|||
testKnowsAddrs(t, n1, n2p, n2.Peerstore().Addresses(n2p)) // has them
|
|||
testKnowsAddrs(t, n2, n1p, []ma.Multiaddr{}) // nothing
|
|||
|
|||
if err := n1.DialPeer(ctx, n2p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// we need to wait here if Dial returns before ID service is finished.
|
|||
if postDialWait > 0 { |
|||
<-time.After(postDialWait) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// the IDService should be opened automatically, by the network.
|
|||
// what we should see now is that both peers know about each others listen addresses.
|
|||
testKnowsAddrs(t, n1, n2p, n2.Peerstore().Addresses(n2p)) // has them
|
|||
testHasProtocolVersions(t, n1, n2p) |
|||
|
|||
// now, this wait we do have to do. it's the wait for the Listening side
|
|||
// to be done identifying the connection.
|
|||
c := n2.ConnsToPeer(n1.LocalPeer()) |
|||
if len(c) < 1 { |
|||
t.Fatal("should have connection by now at least.") |
|||
} |
|||
<-n2.IdentifyProtocol().IdentifyWait(c[0]) |
|||
|
|||
// and the protocol versions.
|
|||
testKnowsAddrs(t, n2, n1p, n1.Peerstore().Addresses(n1p)) // has them
|
|||
testHasProtocolVersions(t, n2, n1p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func testKnowsAddrs(t *testing.T, n inet.Network, p peer.ID, expected []ma.Multiaddr) { |
|||
actual := n.Peerstore().Addresses(p) |
|||
|
|||
if len(actual) != len(expected) { |
|||
t.Error("dont have the same addresses") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
have := map[string]struct{}{} |
|||
for _, addr := range actual { |
|||
have[addr.String()] = struct{}{} |
|||
} |
|||
for _, addr := range expected { |
|||
if _, found := have[addr.String()]; !found { |
|||
t.Errorf("%s did not have addr for %s: %s", n.LocalPeer(), p, addr) |
|||
// panic("ahhhhhhh")
|
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func testHasProtocolVersions(t *testing.T, n inet.Network, p peer.ID) { |
|||
v, err := n.Peerstore().Get(p, "ProtocolVersion") |
|||
if v == nil { |
|||
t.Error("no protocol version") |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
if v.(string) != handshake.IpfsVersion.String() { |
|||
t.Error("protocol mismatch", err) |
|||
} |
|||
v, err = n.Peerstore().Get(p, "AgentVersion") |
|||
if v.(string) != handshake.ClientVersion { |
|||
t.Error("agent version mismatch", err) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// TestIDServiceWait gives the ID service 100ms to finish after dialing
|
|||
// this is becasue it used to be concurrent. Now, Dial wait till the
|
|||
// id service is done.
|
|||
func TestIDServiceWait(t *testing.T) { |
|||
N := 3 |
|||
for i := 0; i < N; i++ { |
|||
subtestIDService(t, 100*time.Millisecond) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestIDServiceNoWait(t *testing.T) { |
|||
N := 3 |
|||
for i := 0; i < N; i++ { |
|||
subtestIDService(t, 0) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,156 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mux |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"io" |
|||
"sync" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
lgbl "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog/loggables" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = eventlog.Logger("net/mux") |
|||
|
|||
// Mux provides simple stream multixplexing.
|
|||
// It helps you precisely when:
|
|||
// * You have many streams
|
|||
// * You have function handlers
|
|||
//
|
|||
// It contains the handlers for each protocol accepted.
|
|||
// It dispatches handlers for streams opened by remote peers.
|
|||
//
|
|||
// We use a totally ad-hoc encoding:
|
|||
// <1 byte length in bytes><string name>
|
|||
// So "bitswap" is 0x0762697473776170
|
|||
//
|
|||
// NOTE: only the dialer specifies this muxing line.
|
|||
// This is because we're using Streams :)
|
|||
//
|
|||
// WARNING: this datastructure IS NOT threadsafe.
|
|||
// do not modify it once the network is using it.
|
|||
type Mux struct { |
|||
Default inet.StreamHandler // handles unknown protocols.
|
|||
Handlers inet.StreamHandlerMap |
|||
|
|||
sync.RWMutex |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Protocols returns the list of protocols this muxer has handlers for
|
|||
func (m *Mux) Protocols() []inet.ProtocolID { |
|||
m.RLock() |
|||
l := make([]inet.ProtocolID, 0, len(m.Handlers)) |
|||
for p := range m.Handlers { |
|||
l = append(l, p) |
|||
} |
|||
m.RUnlock() |
|||
return l |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ReadProtocolHeader reads the stream and returns the next Handler function
|
|||
// according to the muxer encoding.
|
|||
func (m *Mux) ReadProtocolHeader(s io.Reader) (string, inet.StreamHandler, error) { |
|||
// log.Error("ReadProtocolHeader")
|
|||
name, err := ReadLengthPrefix(s) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return "", nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// log.Debug("ReadProtocolHeader got:", name)
|
|||
m.RLock() |
|||
h, found := m.Handlers[inet.ProtocolID(name)] |
|||
m.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
switch { |
|||
case !found && m.Default != nil: |
|||
return name, m.Default, nil |
|||
case !found && m.Default == nil: |
|||
return name, nil, fmt.Errorf("%s no handler with name: %s (%d)", m, name, len(name)) |
|||
default: |
|||
return name, h, nil |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// String returns the muxer's printing representation
|
|||
func (m *Mux) String() string { |
|||
m.RLock() |
|||
defer m.RUnlock() |
|||
return fmt.Sprintf("<Muxer %p %d>", m, len(m.Handlers)) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// SetHandler sets the protocol handler on the Network's Muxer.
|
|||
// This operation is threadsafe.
|
|||
func (m *Mux) SetHandler(p inet.ProtocolID, h inet.StreamHandler) { |
|||
log.Debugf("%s setting handler for protocol: %s (%d)", m, p, len(p)) |
|||
m.Lock() |
|||
m.Handlers[p] = h |
|||
m.Unlock() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Handle reads the next name off the Stream, and calls a handler function
|
|||
// This is done in its own goroutine, to avoid blocking the caller.
|
|||
func (m *Mux) Handle(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
go m.HandleSync(s) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// HandleSync reads the next name off the Stream, and calls a handler function
|
|||
// This is done synchronously. The handler function will return before
|
|||
// HandleSync returns.
|
|||
func (m *Mux) HandleSync(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
|
|||
name, handler, err := m.ReadProtocolHeader(s) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
err = fmt.Errorf("protocol mux error: %s", err) |
|||
log.Error(err) |
|||
log.Event(ctx, "muxError", lgbl.Error(err)) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Infof("muxer handle protocol: %s", name) |
|||
log.Event(ctx, "muxHandle", eventlog.Metadata{"protocol": name}) |
|||
handler(s) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ReadLengthPrefix reads the name from Reader with a length-byte-prefix.
|
|||
func ReadLengthPrefix(r io.Reader) (string, error) { |
|||
// c-string identifier
|
|||
// the first byte is our length
|
|||
l := make([]byte, 1) |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, l); err != nil { |
|||
return "", err |
|||
} |
|||
length := int(l[0]) |
|||
|
|||
// the next are our identifier
|
|||
name := make([]byte, length) |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, name); err != nil { |
|||
return "", err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return string(name), nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// WriteLengthPrefix writes the name into Writer with a length-byte-prefix.
|
|||
func WriteLengthPrefix(w io.Writer, name string) error { |
|||
// log.Error("WriteLengthPrefix", name)
|
|||
s := make([]byte, len(name)+1) |
|||
s[0] = byte(len(name)) |
|||
copy(s[1:], []byte(name)) |
|||
|
|||
_, err := w.Write(s) |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// WriteProtocolHeader defines how a protocol is written into the header of
|
|||
// a stream. This is so the muxer can multiplex between services.
|
|||
func WriteProtocolHeader(pr inet.ProtocolID, s inet.Stream) error { |
|||
if pr != "" { // only write proper protocol headers
|
|||
if err := WriteLengthPrefix(s, string(pr)); err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,65 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mux |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"bytes" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var testCases = map[string]string{ |
|||
"bitswap": "\u0007bitswap", |
|||
"dht": "\u0003dht", |
|||
"ipfs": "\u0004ipfs", |
|||
"ipfsdksnafkasnfkdajfkdajfdsjadosiaaodjasofdias": ".ipfsdksnafkasnfkdajfkdajfdsjadosiaaodjasofdias", |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestWrite(t *testing.T) { |
|||
for k, v := range testCases { |
|||
var buf bytes.Buffer |
|||
WriteLengthPrefix(&buf, k) |
|||
|
|||
v2 := buf.Bytes() |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(v2, []byte(v)) { |
|||
t.Errorf("failed: %s - %v != %v", k, []byte(v), v2) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestHandler(t *testing.T) { |
|||
|
|||
outs := make(chan string, 10) |
|||
|
|||
h := func(n string) func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
return func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
outs <- n |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
m := Mux{Handlers: inet.StreamHandlerMap{}} |
|||
m.Default = h("default") |
|||
m.Handlers["dht"] = h("bitswap") |
|||
// m.Handlers["ipfs"] = h("bitswap") // default!
|
|||
m.Handlers["bitswap"] = h("bitswap") |
|||
m.Handlers["ipfsdksnafkasnfkdajfkdajfdsjadosiaaodjasofdias"] = h("bitswap") |
|||
|
|||
for k, v := range testCases { |
|||
var buf bytes.Buffer |
|||
if _, err := buf.Write([]byte(v)); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
name, _, err := m.ReadProtocolHeader(&buf) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if name != k { |
|||
t.Errorf("name mismatch: %s != %s", k, name) |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,159 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package relay |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"io" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ctxgroup "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-ctxgroup" |
|||
mh "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multihash" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = eventlog.Logger("relay") |
|||
|
|||
// ProtocolRelay is the ProtocolID of the Relay Service.
|
|||
const ProtocolRelay inet.ProtocolID = "/ipfs/relay" |
|||
|
|||
// Relay is a structure that implements ProtocolRelay.
|
|||
// It is a simple relay service which forwards traffic
|
|||
// between two directly connected peers.
|
|||
//
|
|||
// the protocol is very simple:
|
|||
//
|
|||
// /ipfs/relay\n
|
|||
// <multihash src id>
|
|||
// <multihash dst id>
|
|||
// <data stream>
|
|||
//
|
|||
type RelayService struct { |
|||
Network inet.Network |
|||
handler inet.StreamHandler // for streams sent to us locally.
|
|||
|
|||
cg ctxgroup.ContextGroup |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func NewRelayService(ctx context.Context, n inet.Network, sh inet.StreamHandler) *RelayService { |
|||
s := &RelayService{ |
|||
Network: n, |
|||
handler: sh, |
|||
cg: ctxgroup.WithContext(ctx), |
|||
} |
|||
n.SetHandler(inet.ProtocolRelay, s.requestHandler) |
|||
return s |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// requestHandler is the function called by clients
|
|||
func (rs *RelayService) requestHandler(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
if err := rs.handleStream(s); err != nil { |
|||
log.Error("RelayService error:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// handleStream is our own handler, which returns an error for simplicity.
|
|||
func (rs *RelayService) handleStream(s inet.Stream) error { |
|||
defer s.Close() |
|||
|
|||
// read the header (src and dst peer.IDs)
|
|||
src, dst, err := ReadHeader(s) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return fmt.Errorf("stream with bad header: %s", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
local := rs.Network.LocalPeer() |
|||
|
|||
switch { |
|||
case src == local: |
|||
return fmt.Errorf("relaying from self") |
|||
case dst == local: // it's for us! yaaay.
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s consuming stream from %s", rs.Network.LocalPeer(), src) |
|||
return rs.consumeStream(s) |
|||
default: // src and dst are not local. relay it.
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s relaying stream %s <--> %s", rs.Network.LocalPeer(), src, dst) |
|||
return rs.pipeStream(src, dst, s) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// consumeStream connects streams directed to the local peer
|
|||
// to our handler, with the header now stripped (read).
|
|||
func (rs *RelayService) consumeStream(s inet.Stream) error { |
|||
rs.handler(s) // boom.
|
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// pipeStream relays over a stream to a remote peer. It's like `cat`
|
|||
func (rs *RelayService) pipeStream(src, dst peer.ID, s inet.Stream) error { |
|||
s2, err := rs.openStreamToPeer(dst) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return fmt.Errorf("failed to open stream to peer: %s -- %s", dst, err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if err := WriteHeader(s2, src, dst); err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// connect the series of tubes.
|
|||
done := make(chan retio, 2) |
|||
go func() { |
|||
n, err := io.Copy(s2, s) |
|||
done <- retio{n, err} |
|||
}() |
|||
go func() { |
|||
n, err := io.Copy(s, s2) |
|||
done <- retio{n, err} |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
r1 := <-done |
|||
r2 := <-done |
|||
log.Infof("relayed %d/%d bytes between %s and %s", r1.n, r2.n, src, dst) |
|||
|
|||
if r1.err != nil { |
|||
return r1.err |
|||
} |
|||
return r2.err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// openStreamToPeer opens a pipe to a remote endpoint
|
|||
// for now, can only open streams to directly connected peers.
|
|||
// maybe we can do some routing later on.
|
|||
func (rs *RelayService) openStreamToPeer(p peer.ID) (inet.Stream, error) { |
|||
return rs.Network.NewStream(ProtocolRelay, p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func ReadHeader(r io.Reader) (src, dst peer.ID, err error) { |
|||
|
|||
mhr := mh.NewReader(r) |
|||
|
|||
s, err := mhr.ReadMultihash() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return "", "", err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
d, err := mhr.ReadMultihash() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return "", "", err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return peer.ID(s), peer.ID(d), nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func WriteHeader(w io.Writer, src, dst peer.ID) error { |
|||
// write header to w.
|
|||
mhw := mh.NewWriter(w) |
|||
if err := mhw.WriteMultihash(mh.Multihash(src)); err != nil { |
|||
return fmt.Errorf("failed to write relay header: %s -- %s", dst, err) |
|||
} |
|||
if err := mhw.WriteMultihash(mh.Multihash(dst)); err != nil { |
|||
return fmt.Errorf("failed to write relay header: %s -- %s", dst, err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
type retio struct { |
|||
n int64 |
|||
err error |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,309 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package relay_test |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"io" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
mux "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/services/mux" |
|||
relay "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/services/relay" |
|||
netutil "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/swarmnet/util" |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = eventlog.Logger("relay_test") |
|||
|
|||
func TestRelaySimple(t *testing.T) { |
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
|
|||
// these networks have the relay service wired in already.
|
|||
n1 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n2 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n3 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
n1p := n1.LocalPeer() |
|||
n2p := n2.LocalPeer() |
|||
n3p := n3.LocalPeer() |
|||
|
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n2, n1) |
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n2, n3) |
|||
|
|||
if err := n1.DialPeer(ctx, n2p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
if err := n3.DialPeer(ctx, n2p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// setup handler on n3 to copy everything over to the pipe.
|
|||
piper, pipew := io.Pipe() |
|||
n3.SetHandler(inet.ProtocolTesting, func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
log.Debug("relay stream opened to n3!") |
|||
log.Debug("piping and echoing everything") |
|||
w := io.MultiWriter(s, pipew) |
|||
io.Copy(w, s) |
|||
log.Debug("closing stream") |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
}) |
|||
|
|||
// ok, now we can try to relay n1--->n2--->n3.
|
|||
log.Debug("open relay stream") |
|||
s, err := n1.NewStream(relay.ProtocolRelay, n2p) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok first thing we write the relay header n1->n3
|
|||
log.Debug("write relay header") |
|||
if err := relay.WriteHeader(s, n1p, n3p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok now the header's there, we can write the next protocol header.
|
|||
log.Debug("write testing header") |
|||
if err := mux.WriteProtocolHeader(inet.ProtocolTesting, s); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// okay, now we should be able to write text, and read it out.
|
|||
buf1 := []byte("abcdefghij") |
|||
buf2 := make([]byte, 10) |
|||
buf3 := make([]byte, 10) |
|||
log.Debug("write in some text.") |
|||
if _, err := s.Write(buf1); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// read it out from the pipe.
|
|||
log.Debug("read it out from the pipe.") |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(piper, buf2); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if string(buf1) != string(buf2) { |
|||
t.Fatal("should've gotten that text out of the pipe") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// read it out from the stream (echoed)
|
|||
log.Debug("read it out from the stream (echoed).") |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(s, buf3); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if string(buf1) != string(buf3) { |
|||
t.Fatal("should've gotten that text out of the stream") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// sweet. relay works.
|
|||
log.Debug("sweet, relay works.") |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestRelayAcrossFour(t *testing.T) { |
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
|
|||
// these networks have the relay service wired in already.
|
|||
n1 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n2 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n3 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n4 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n5 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
n1p := n1.LocalPeer() |
|||
n2p := n2.LocalPeer() |
|||
n3p := n3.LocalPeer() |
|||
n4p := n4.LocalPeer() |
|||
n5p := n5.LocalPeer() |
|||
|
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n2, n1) |
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n2, n3) |
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n4, n3) |
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n4, n5) |
|||
|
|||
if err := n1.DialPeer(ctx, n2p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
if err := n3.DialPeer(ctx, n2p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
if err := n3.DialPeer(ctx, n4p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
if err := n5.DialPeer(ctx, n4p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// setup handler on n5 to copy everything over to the pipe.
|
|||
piper, pipew := io.Pipe() |
|||
n5.SetHandler(inet.ProtocolTesting, func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
log.Debug("relay stream opened to n5!") |
|||
log.Debug("piping and echoing everything") |
|||
w := io.MultiWriter(s, pipew) |
|||
io.Copy(w, s) |
|||
log.Debug("closing stream") |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
}) |
|||
|
|||
// ok, now we can try to relay n1--->n2--->n3--->n4--->n5
|
|||
log.Debug("open relay stream") |
|||
s, err := n1.NewStream(relay.ProtocolRelay, n2p) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("write relay header n1->n3 (%s -> %s)", n1p, n3p) |
|||
if err := relay.WriteHeader(s, n1p, n3p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("write relay header n1->n4 (%s -> %s)", n1p, n4p) |
|||
if err := mux.WriteProtocolHeader(relay.ProtocolRelay, s); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if err := relay.WriteHeader(s, n1p, n4p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("write relay header n1->n5 (%s -> %s)", n1p, n5p) |
|||
if err := mux.WriteProtocolHeader(relay.ProtocolRelay, s); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if err := relay.WriteHeader(s, n1p, n5p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok now the header's there, we can write the next protocol header.
|
|||
log.Debug("write testing header") |
|||
if err := mux.WriteProtocolHeader(inet.ProtocolTesting, s); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// okay, now we should be able to write text, and read it out.
|
|||
buf1 := []byte("abcdefghij") |
|||
buf2 := make([]byte, 10) |
|||
buf3 := make([]byte, 10) |
|||
log.Debug("write in some text.") |
|||
if _, err := s.Write(buf1); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// read it out from the pipe.
|
|||
log.Debug("read it out from the pipe.") |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(piper, buf2); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if string(buf1) != string(buf2) { |
|||
t.Fatal("should've gotten that text out of the pipe") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// read it out from the stream (echoed)
|
|||
log.Debug("read it out from the stream (echoed).") |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(s, buf3); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if string(buf1) != string(buf3) { |
|||
t.Fatal("should've gotten that text out of the stream") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// sweet. relay works.
|
|||
log.Debug("sweet, relaying across 4 works.") |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestRelayStress(t *testing.T) { |
|||
buflen := 1 << 18 |
|||
iterations := 10 |
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
|
|||
// these networks have the relay service wired in already.
|
|||
n1 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n2 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
n3 := netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
n1p := n1.LocalPeer() |
|||
n2p := n2.LocalPeer() |
|||
n3p := n3.LocalPeer() |
|||
|
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n2, n1) |
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(n2, n3) |
|||
|
|||
if err := n1.DialPeer(ctx, n2p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
if err := n3.DialPeer(ctx, n2p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// setup handler on n3 to copy everything over to the pipe.
|
|||
piper, pipew := io.Pipe() |
|||
n3.SetHandler(inet.ProtocolTesting, func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
log.Debug("relay stream opened to n3!") |
|||
log.Debug("piping and echoing everything") |
|||
w := io.MultiWriter(s, pipew) |
|||
io.Copy(w, s) |
|||
log.Debug("closing stream") |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
}) |
|||
|
|||
// ok, now we can try to relay n1--->n2--->n3.
|
|||
log.Debug("open relay stream") |
|||
s, err := n1.NewStream(relay.ProtocolRelay, n2p) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok first thing we write the relay header n1->n3
|
|||
log.Debug("write relay header") |
|||
if err := relay.WriteHeader(s, n1p, n3p); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok now the header's there, we can write the next protocol header.
|
|||
log.Debug("write testing header") |
|||
if err := mux.WriteProtocolHeader(inet.ProtocolTesting, s); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// okay, now write lots of text and read it back out from both
|
|||
// the pipe and the stream.
|
|||
buf1 := make([]byte, buflen) |
|||
buf2 := make([]byte, len(buf1)) |
|||
buf3 := make([]byte, len(buf1)) |
|||
|
|||
fillbuf := func(buf []byte, b byte) { |
|||
for i := range buf { |
|||
buf[i] = b |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < iterations; i++ { |
|||
fillbuf(buf1, byte(int('a')+i)) |
|||
log.Debugf("writing %d bytes (%d/%d)", len(buf1), i, iterations) |
|||
if _, err := s.Write(buf1); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debug("read it out from the pipe.") |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(piper, buf2); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if string(buf1) != string(buf2) { |
|||
t.Fatal("should've gotten that text out of the pipe") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// read it out from the stream (echoed)
|
|||
log.Debug("read it out from the stream (echoed).") |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(s, buf3); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if string(buf1) != string(buf3) { |
|||
t.Fatal("should've gotten that text out of the stream") |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debug("sweet, relay works under stress.") |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,309 +0,0 @@ |
|||
// Package net provides an interface for ipfs to interact with the network through
|
|||
package net |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
ids "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/services/identify" |
|||
mux "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/services/mux" |
|||
relay "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/services/relay" |
|||
swarm "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/swarm" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ctxgroup "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-ctxgroup" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = eventlog.Logger("net/mux") |
|||
|
|||
type stream swarm.Stream |
|||
|
|||
func (s *stream) SwarmStream() *swarm.Stream { |
|||
return (*swarm.Stream)(s) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Conn returns the connection this stream is part of.
|
|||
func (s *stream) Conn() inet.Conn { |
|||
c := s.SwarmStream().Conn() |
|||
return (*conn_)(c) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Conn returns the connection this stream is part of.
|
|||
func (s *stream) Close() error { |
|||
return s.SwarmStream().Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Read reads bytes from a stream.
|
|||
func (s *stream) Read(p []byte) (n int, err error) { |
|||
return s.SwarmStream().Read(p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Write writes bytes to a stream, flushing for each call.
|
|||
func (s *stream) Write(p []byte) (n int, err error) { |
|||
return s.SwarmStream().Write(p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
type conn_ swarm.Conn |
|||
|
|||
func (s *conn_) String() string { |
|||
return s.SwarmConn().String() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn_) SwarmConn() *swarm.Conn { |
|||
return (*swarm.Conn)(c) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn_) NewStreamWithProtocol(pr inet.ProtocolID) (inet.Stream, error) { |
|||
s, err := (*swarm.Conn)(c).NewStream() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
ss := (*stream)(s) |
|||
|
|||
if err := mux.WriteProtocolHeader(pr, ss); err != nil { |
|||
ss.Close() |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return ss, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn_) LocalMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.SwarmConn().LocalMultiaddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn_) RemoteMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.SwarmConn().RemoteMultiaddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn_) LocalPeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.SwarmConn().LocalPeer() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn_) RemotePeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.SwarmConn().RemotePeer() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn_) LocalPrivateKey() ic.PrivKey { |
|||
return c.SwarmConn().LocalPrivateKey() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn_) RemotePublicKey() ic.PubKey { |
|||
return c.SwarmConn().RemotePublicKey() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Network implements the inet.Network interface.
|
|||
// It uses a swarm to connect to remote hosts.
|
|||
type Network struct { |
|||
local peer.ID // local peer
|
|||
ps peer.Peerstore |
|||
|
|||
swarm *swarm.Swarm // peer connection multiplexing
|
|||
mux mux.Mux // protocol multiplexing
|
|||
ids *ids.IDService |
|||
relay *relay.RelayService |
|||
|
|||
cg ctxgroup.ContextGroup // for Context closing
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NewNetwork constructs a new network and starts listening on given addresses.
|
|||
func NewNetwork(ctx context.Context, listen []ma.Multiaddr, local peer.ID, |
|||
peers peer.Peerstore) (*Network, error) { |
|||
|
|||
s, err := swarm.NewSwarm(ctx, listen, local, peers) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
n := &Network{ |
|||
local: local, |
|||
swarm: s, |
|||
mux: mux.Mux{Handlers: inet.StreamHandlerMap{}}, |
|||
cg: ctxgroup.WithContext(ctx), |
|||
ps: peers, |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
n.cg.SetTeardown(n.close) |
|||
n.cg.AddChildGroup(s.CtxGroup()) |
|||
|
|||
s.SetStreamHandler(func(s *swarm.Stream) { |
|||
n.mux.Handle((*stream)(s)) |
|||
}) |
|||
|
|||
// setup ProtocolIdentify to immediately "asks the other side about them"
|
|||
n.ids = ids.NewIDService(n) |
|||
s.SetConnHandler(n.newConnHandler) |
|||
|
|||
// setup ProtocolRelay to allow traffic relaying.
|
|||
// Feed things we get for ourselves into the muxer.
|
|||
n.relay = relay.NewRelayService(n.cg.Context(), n, n.mux.HandleSync) |
|||
return n, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (n *Network) newConnHandler(c *swarm.Conn) { |
|||
cc := (*conn_)(c) |
|||
n.ids.IdentifyConn(cc) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// DialPeer attempts to establish a connection to a given peer.
|
|||
// Respects the context.
|
|||
func (n *Network) DialPeer(ctx context.Context, p peer.ID) error { |
|||
log.Debugf("[%s] network dialing peer [%s]", n.local, p) |
|||
sc, err := n.swarm.Dial(ctx, p) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// identify the connection before returning.
|
|||
done := make(chan struct{}) |
|||
go func() { |
|||
n.ids.IdentifyConn((*conn_)(sc)) |
|||
close(done) |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
// respect don contexteone
|
|||
select { |
|||
case <-done: |
|||
case <-ctx.Done(): |
|||
return ctx.Err() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("network for %s finished dialing %s", n.local, p) |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Protocols returns the ProtocolIDs of all the registered handlers.
|
|||
func (n *Network) Protocols() []inet.ProtocolID { |
|||
return n.mux.Protocols() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// CtxGroup returns the network's ContextGroup
|
|||
func (n *Network) CtxGroup() ctxgroup.ContextGroup { |
|||
return n.cg |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Swarm returns the network's peerstream.Swarm
|
|||
func (n *Network) Swarm() *swarm.Swarm { |
|||
return n.Swarm() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer the network's LocalPeer
|
|||
func (n *Network) LocalPeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return n.swarm.LocalPeer() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Peers returns the connected peers
|
|||
func (n *Network) Peers() []peer.ID { |
|||
return n.swarm.Peers() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Peers returns the connected peers
|
|||
func (n *Network) Peerstore() peer.Peerstore { |
|||
return n.ps |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Conns returns the connected peers
|
|||
func (n *Network) Conns() []inet.Conn { |
|||
conns1 := n.swarm.Connections() |
|||
out := make([]inet.Conn, len(conns1)) |
|||
for i, c := range conns1 { |
|||
out[i] = (*conn_)(c) |
|||
} |
|||
return out |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ConnsToPeer returns the connections in this Netowrk for given peer.
|
|||
func (n *Network) ConnsToPeer(p peer.ID) []inet.Conn { |
|||
conns1 := n.swarm.ConnectionsToPeer(p) |
|||
out := make([]inet.Conn, len(conns1)) |
|||
for i, c := range conns1 { |
|||
out[i] = (*conn_)(c) |
|||
} |
|||
return out |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ClosePeer connection to peer
|
|||
func (n *Network) ClosePeer(p peer.ID) error { |
|||
return n.swarm.CloseConnection(p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// close is the real teardown function
|
|||
func (n *Network) close() error { |
|||
return n.swarm.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Close calls the ContextCloser func
|
|||
func (n *Network) Close() error { |
|||
return n.cg.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// BandwidthTotals returns the total amount of bandwidth transferred
|
|||
func (n *Network) BandwidthTotals() (in uint64, out uint64) { |
|||
// need to implement this. probably best to do it in swarm this time.
|
|||
// need a "metrics" object
|
|||
return 0, 0 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ListenAddresses returns a list of addresses at which this network listens.
|
|||
func (n *Network) ListenAddresses() []ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return n.swarm.ListenAddresses() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// InterfaceListenAddresses returns a list of addresses at which this network
|
|||
// listens. It expands "any interface" addresses (/ip4/0.0.0.0, /ip6/::) to
|
|||
// use the known local interfaces.
|
|||
func (n *Network) InterfaceListenAddresses() ([]ma.Multiaddr, error) { |
|||
return swarm.InterfaceListenAddresses(n.swarm) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Connectedness returns a state signaling connection capabilities
|
|||
// For now only returns Connected || NotConnected. Expand into more later.
|
|||
func (n *Network) Connectedness(p peer.ID) inet.Connectedness { |
|||
c := n.swarm.ConnectionsToPeer(p) |
|||
if c != nil && len(c) > 0 { |
|||
return inet.Connected |
|||
} |
|||
return inet.NotConnected |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NewStream returns a new stream to given peer p.
|
|||
// If there is no connection to p, attempts to create one.
|
|||
// If ProtocolID is "", writes no header.
|
|||
func (n *Network) NewStream(pr inet.ProtocolID, p peer.ID) (inet.Stream, error) { |
|||
log.Debugf("[%s] network opening stream to peer [%s]: %s", n.local, p, pr) |
|||
s, err := n.swarm.NewStreamWithPeer(p) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
ss := (*stream)(s) |
|||
|
|||
if err := mux.WriteProtocolHeader(pr, ss); err != nil { |
|||
ss.Close() |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return ss, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// SetHandler sets the protocol handler on the Network's Muxer.
|
|||
// This operation is threadsafe.
|
|||
func (n *Network) SetHandler(p inet.ProtocolID, h inet.StreamHandler) { |
|||
n.mux.SetHandler(p, h) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// String returns a string representation of Network.
|
|||
func (n *Network) String() string { |
|||
return fmt.Sprintf("<Network %s>", n.LocalPeer()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// IdentifyProtocol returns the network's IDService
|
|||
func (n *Network) IdentifyProtocol() *ids.IDService { |
|||
return n.ids |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,78 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package net_test |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
netutil "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/swarmnet/util" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// TestConnectednessCorrect starts a few networks, connects a few
|
|||
// and tests Connectedness value is correct.
|
|||
func TestConnectednessCorrect(t *testing.T) { |
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
|
|||
nets := make([]inet.Network, 4) |
|||
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ { |
|||
nets[i] = netutil.GenNetwork(t, ctx) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// connect 0-1, 0-2, 0-3, 1-2, 2-3
|
|||
|
|||
dial := func(a, b inet.Network) { |
|||
netutil.DivulgeAddresses(b, a) |
|||
if err := a.DialPeer(ctx, b.LocalPeer()); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("Failed to dial: %s", err) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
dial(nets[0], nets[1]) |
|||
dial(nets[0], nets[3]) |
|||
dial(nets[1], nets[2]) |
|||
dial(nets[3], nets[2]) |
|||
|
|||
// there's something wrong with dial, i think. it's not finishing
|
|||
// completely. there must be some async stuff.
|
|||
<-time.After(100 * time.Millisecond) |
|||
|
|||
// test those connected show up correctly
|
|||
|
|||
// test connected
|
|||
expectConnectedness(t, nets[0], nets[1], inet.Connected) |
|||
expectConnectedness(t, nets[0], nets[3], inet.Connected) |
|||
expectConnectedness(t, nets[1], nets[2], inet.Connected) |
|||
expectConnectedness(t, nets[3], nets[2], inet.Connected) |
|||
|
|||
// test not connected
|
|||
expectConnectedness(t, nets[0], nets[2], inet.NotConnected) |
|||
expectConnectedness(t, nets[1], nets[3], inet.NotConnected) |
|||
|
|||
for _, n := range nets { |
|||
n.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func expectConnectedness(t *testing.T, a, b inet.Network, expected inet.Connectedness) { |
|||
es := "%s is connected to %s, but Connectedness incorrect. %s %s" |
|||
if a.Connectedness(b.LocalPeer()) != expected { |
|||
t.Errorf(es, a, b, printConns(a), printConns(b)) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// test symmetric case
|
|||
if b.Connectedness(a.LocalPeer()) != expected { |
|||
t.Errorf(es, b, a, printConns(b), printConns(a)) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func printConns(n inet.Network) string { |
|||
s := fmt.Sprintf("Connections in %s:\n", n) |
|||
for _, c := range n.Conns() { |
|||
s = s + fmt.Sprintf("- %s\n", c) |
|||
} |
|||
return s |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package testutil |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"testing" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net" |
|||
sn "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/swarmnet" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
tu "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/testutil" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
func GenNetwork(t *testing.T, ctx context.Context) *sn.Network { |
|||
p := tu.RandPeerNetParamsOrFatal(t) |
|||
ps := peer.NewPeerstore() |
|||
ps.AddAddress(p.ID, p.Addr) |
|||
ps.AddPubKey(p.ID, p.PubKey) |
|||
ps.AddPrivKey(p.ID, p.PrivKey) |
|||
n, err := sn.NewNetwork(ctx, ps.Addresses(p.ID), p.ID, ps) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
return n |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func DivulgeAddresses(a, b inet.Network) { |
|||
id := a.LocalPeer() |
|||
addrs := a.Peerstore().Addresses(id) |
|||
b.Peerstore().AddAddresses(id, addrs) |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,17 +0,0 @@ |
|||
# Network |
|||
|
|||
The IPFS Network package handles all of the peer-to-peer networking. It connects to other hosts, it encrypts communications, it muxes messages between the network's client services and target hosts. It has multiple subcomponents: |
|||
|
|||
- `Conn` - a connection to a single Peer |
|||
- `MultiConn` - a set of connections to a single Peer |
|||
- `SecureConn` - an encrypted (tls-like) connection |
|||
- `Swarm` - holds connections to Peers, multiplexes from/to each `MultiConn` |
|||
- `Muxer` - multiplexes between `Services` and `Swarm`. Handles `Requet/Reply`. |
|||
- `Service` - connects between an outside client service and Network. |
|||
- `Handler` - the client service part that handles requests |
|||
|
|||
It looks a bit like this: |
|||
|
|||
<center> |
|||
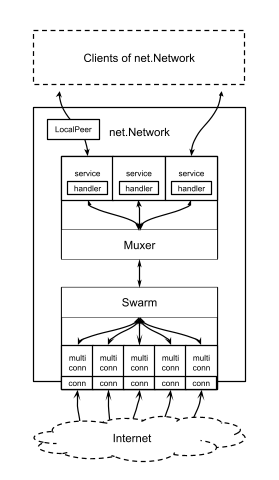 |
|||
</center> |
|||
@ -1,157 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package conn |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"net" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
msgio "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-msgio" |
|||
mpool "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-msgio/mpool" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
manet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr-net" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
u "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util" |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = eventlog.Logger("conn") |
|||
|
|||
// ReleaseBuffer puts the given byte array back into the buffer pool,
|
|||
// first verifying that it is the correct size
|
|||
func ReleaseBuffer(b []byte) { |
|||
log.Debugf("Releasing buffer! (cap,size = %d, %d)", cap(b), len(b)) |
|||
mpool.ByteSlicePool.Put(uint32(cap(b)), b) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// singleConn represents a single connection to another Peer (IPFS Node).
|
|||
type singleConn struct { |
|||
local peer.ID |
|||
remote peer.ID |
|||
maconn manet.Conn |
|||
msgrw msgio.ReadWriteCloser |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// newConn constructs a new connection
|
|||
func newSingleConn(ctx context.Context, local, remote peer.ID, maconn manet.Conn) (Conn, error) { |
|||
|
|||
conn := &singleConn{ |
|||
local: local, |
|||
remote: remote, |
|||
maconn: maconn, |
|||
msgrw: msgio.NewReadWriter(maconn), |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("newSingleConn %p: %v to %v", conn, local, remote) |
|||
return conn, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// close is the internal close function, called by ContextCloser.Close
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) Close() error { |
|||
log.Debugf("%s closing Conn with %s", c.local, c.remote) |
|||
// close underlying connection
|
|||
return c.msgrw.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ID is an identifier unique to this connection.
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) ID() string { |
|||
return ID(c) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) String() string { |
|||
return String(c, "singleConn") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) LocalAddr() net.Addr { |
|||
return c.maconn.LocalAddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) RemoteAddr() net.Addr { |
|||
return c.maconn.RemoteAddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) LocalPrivateKey() ic.PrivKey { |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) RemotePublicKey() ic.PubKey { |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) SetDeadline(t time.Time) error { |
|||
return c.maconn.SetDeadline(t) |
|||
} |
|||
func (c *singleConn) SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error { |
|||
return c.maconn.SetReadDeadline(t) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error { |
|||
return c.maconn.SetWriteDeadline(t) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalMultiaddr is the Multiaddr on this side
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) LocalMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.maconn.LocalMultiaddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemoteMultiaddr is the Multiaddr on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) RemoteMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.maconn.RemoteMultiaddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer is the Peer on this side
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) LocalPeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.local |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemotePeer is the Peer on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) RemotePeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.remote |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Read reads data, net.Conn style
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) Read(buf []byte) (int, error) { |
|||
return c.msgrw.Read(buf) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Write writes data, net.Conn style
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) Write(buf []byte) (int, error) { |
|||
return c.msgrw.Write(buf) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) NextMsgLen() (int, error) { |
|||
return c.msgrw.NextMsgLen() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ReadMsg reads data, net.Conn style
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) ReadMsg() ([]byte, error) { |
|||
return c.msgrw.ReadMsg() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// WriteMsg writes data, net.Conn style
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) WriteMsg(buf []byte) error { |
|||
return c.msgrw.WriteMsg(buf) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ReleaseMsg releases a buffer
|
|||
func (c *singleConn) ReleaseMsg(m []byte) { |
|||
c.msgrw.ReleaseMsg(m) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ID returns the ID of a given Conn.
|
|||
func ID(c Conn) string { |
|||
l := fmt.Sprintf("%s/%s", c.LocalMultiaddr(), c.LocalPeer().Pretty()) |
|||
r := fmt.Sprintf("%s/%s", c.RemoteMultiaddr(), c.RemotePeer().Pretty()) |
|||
lh := u.Hash([]byte(l)) |
|||
rh := u.Hash([]byte(r)) |
|||
ch := u.XOR(lh, rh) |
|||
return u.Key(ch).Pretty() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// String returns the user-friendly String representation of a conn
|
|||
func String(c Conn, typ string) string { |
|||
return fmt.Sprintf("%s (%s) <-- %s %p --> (%s) %s", |
|||
c.LocalPeer(), c.LocalMultiaddr(), typ, c, c.RemoteMultiaddr(), c.RemotePeer()) |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,122 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package conn |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"bytes" |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"os" |
|||
"runtime" |
|||
"sync" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
func testOneSendRecv(t *testing.T, c1, c2 Conn) { |
|||
log.Debugf("testOneSendRecv from %s to %s", c1.LocalPeer(), c2.LocalPeer()) |
|||
m1 := []byte("hello") |
|||
if err := c1.WriteMsg(m1); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
m2, err := c2.ReadMsg() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(m1, m2) { |
|||
t.Fatal("failed to send: %s %s", m1, m2) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func testNotOneSendRecv(t *testing.T, c1, c2 Conn) { |
|||
m1 := []byte("hello") |
|||
if err := c1.WriteMsg(m1); err == nil { |
|||
t.Fatal("write should have failed", err) |
|||
} |
|||
_, err := c2.ReadMsg() |
|||
if err == nil { |
|||
t.Fatal("read should have failed", err) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestClose(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
|
|||
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background()) |
|||
defer cancel() |
|||
c1, c2, _, _ := setupSingleConn(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
testOneSendRecv(t, c1, c2) |
|||
testOneSendRecv(t, c2, c1) |
|||
|
|||
c1.Close() |
|||
testNotOneSendRecv(t, c1, c2) |
|||
|
|||
c2.Close() |
|||
testNotOneSendRecv(t, c2, c1) |
|||
testNotOneSendRecv(t, c1, c2) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestCloseLeak(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
if testing.Short() { |
|||
t.SkipNow() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if os.Getenv("TRAVIS") == "true" { |
|||
t.Skip("this doesn't work well on travis") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
var wg sync.WaitGroup |
|||
|
|||
runPair := func(num int) { |
|||
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background()) |
|||
c1, c2, _, _ := setupSingleConn(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < num; i++ { |
|||
b1 := []byte(fmt.Sprintf("beep%d", i)) |
|||
c1.WriteMsg(b1) |
|||
b2, err := c2.ReadMsg() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(b1, b2) { |
|||
panic(fmt.Errorf("bytes not equal: %s != %s", b1, b2)) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
b2 = []byte(fmt.Sprintf("boop%d", i)) |
|||
c2.WriteMsg(b2) |
|||
b1, err = c1.ReadMsg() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(b1, b2) { |
|||
panic(fmt.Errorf("bytes not equal: %s != %s", b1, b2)) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
<-time.After(time.Microsecond * 5) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
c1.Close() |
|||
c2.Close() |
|||
cancel() // close the listener
|
|||
wg.Done() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
var cons = 5 |
|||
var msgs = 50 |
|||
log.Debugf("Running %d connections * %d msgs.\n", cons, msgs) |
|||
for i := 0; i < cons; i++ { |
|||
wg.Add(1) |
|||
go runPair(msgs) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("Waiting...\n") |
|||
wg.Wait() |
|||
// done!
|
|||
|
|||
<-time.After(time.Millisecond * 150) |
|||
if runtime.NumGoroutine() > 20 { |
|||
// panic("uncomment me to debug")
|
|||
t.Fatal("leaking goroutines:", runtime.NumGoroutine()) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,131 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package conn |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"strings" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
manet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr-net" |
|||
|
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
debugerror "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/debugerror" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// String returns the string rep of d.
|
|||
func (d *Dialer) String() string { |
|||
return fmt.Sprintf("<Dialer %s %s ...>", d.LocalPeer, d.LocalAddrs[0]) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Dial connects to a peer over a particular address
|
|||
// Ensures raddr is part of peer.Addresses()
|
|||
// Example: d.DialAddr(ctx, peer.Addresses()[0], peer)
|
|||
func (d *Dialer) Dial(ctx context.Context, raddr ma.Multiaddr, remote peer.ID) (Conn, error) { |
|||
|
|||
network, _, err := manet.DialArgs(raddr) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if strings.HasPrefix(raddr.String(), "/ip4/0.0.0.0") { |
|||
return nil, debugerror.Errorf("Attempted to connect to zero address: %s", raddr) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
var laddr ma.Multiaddr |
|||
if len(d.LocalAddrs) > 0 { |
|||
// laddr := MultiaddrNetMatch(raddr, d.LocalAddrs)
|
|||
laddr = NetAddress(network, d.LocalAddrs) |
|||
if laddr == nil { |
|||
return nil, debugerror.Errorf("No local address for network %s", network) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// TODO: try to get reusing addr/ports to work.
|
|||
// madialer := manet.Dialer{LocalAddr: laddr}
|
|||
madialer := manet.Dialer{} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s dialing %s %s", d.LocalPeer, remote, raddr) |
|||
maconn, err := madialer.Dial(raddr) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
var connOut Conn |
|||
var errOut error |
|||
done := make(chan struct{}) |
|||
|
|||
// do it async to ensure we respect don contexteone
|
|||
go func() { |
|||
defer func() { done <- struct{}{} }() |
|||
|
|||
c, err := newSingleConn(ctx, d.LocalPeer, remote, maconn) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
errOut = err |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if d.PrivateKey == nil { |
|||
log.Warning("dialer %s dialing INSECURELY %s at %s!", d, remote, raddr) |
|||
connOut = c |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
c2, err := newSecureConn(ctx, d.PrivateKey, c) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
errOut = err |
|||
c.Close() |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
connOut = c2 |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
select { |
|||
case <-ctx.Done(): |
|||
maconn.Close() |
|||
return nil, ctx.Err() |
|||
case <-done: |
|||
// whew, finished.
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return connOut, errOut |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// MultiaddrProtocolsMatch returns whether two multiaddrs match in protocol stacks.
|
|||
func MultiaddrProtocolsMatch(a, b ma.Multiaddr) bool { |
|||
ap := a.Protocols() |
|||
bp := b.Protocols() |
|||
|
|||
if len(ap) != len(bp) { |
|||
return false |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for i, api := range ap { |
|||
if api != bp[i] { |
|||
return false |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return true |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// MultiaddrNetMatch returns the first Multiaddr found to match network.
|
|||
func MultiaddrNetMatch(tgt ma.Multiaddr, srcs []ma.Multiaddr) ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
for _, a := range srcs { |
|||
if MultiaddrProtocolsMatch(tgt, a) { |
|||
return a |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NetAddress returns the first Multiaddr found for a given network.
|
|||
func NetAddress(n string, addrs []ma.Multiaddr) ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
for _, a := range addrs { |
|||
for _, p := range a.Protocols() { |
|||
if p.Name == n { |
|||
return a |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,165 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package conn |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"io" |
|||
"net" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
tu "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/testutil" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
func echoListen(ctx context.Context, listener Listener) { |
|||
for { |
|||
c, err := listener.Accept() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
|
|||
select { |
|||
case <-ctx.Done(): |
|||
return |
|||
default: |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if ne, ok := err.(net.Error); ok && ne.Temporary() { |
|||
<-time.After(time.Microsecond * 10) |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("echoListen: listener appears to be closing") |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
go echo(c.(Conn)) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func echo(c Conn) { |
|||
io.Copy(c, c) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func setupSecureConn(t *testing.T, ctx context.Context) (a, b Conn, p1, p2 tu.PeerNetParams) { |
|||
return setupConn(t, ctx, true) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func setupSingleConn(t *testing.T, ctx context.Context) (a, b Conn, p1, p2 tu.PeerNetParams) { |
|||
return setupConn(t, ctx, false) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func setupConn(t *testing.T, ctx context.Context, secure bool) (a, b Conn, p1, p2 tu.PeerNetParams) { |
|||
|
|||
p1 = tu.RandPeerNetParamsOrFatal(t) |
|||
p2 = tu.RandPeerNetParamsOrFatal(t) |
|||
laddr := p1.Addr |
|||
|
|||
key1 := p1.PrivKey |
|||
key2 := p2.PrivKey |
|||
if !secure { |
|||
key1 = nil |
|||
key2 = nil |
|||
} |
|||
l1, err := Listen(ctx, laddr, p1.ID, key1) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
d2 := &Dialer{ |
|||
LocalPeer: p2.ID, |
|||
PrivateKey: key2, |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
var c2 Conn |
|||
|
|||
done := make(chan error) |
|||
go func() { |
|||
var err error |
|||
c2, err = d2.Dial(ctx, p1.Addr, p1.ID) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
done <- err |
|||
} |
|||
close(done) |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
c1, err := l1.Accept() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal("failed to accept", err) |
|||
} |
|||
if err := <-done; err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return c1.(Conn), c2, p1, p2 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func testDialer(t *testing.T, secure bool) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
|
|||
p1 := tu.RandPeerNetParamsOrFatal(t) |
|||
p2 := tu.RandPeerNetParamsOrFatal(t) |
|||
|
|||
key1 := p1.PrivKey |
|||
key2 := p2.PrivKey |
|||
if !secure { |
|||
key1 = nil |
|||
key2 = nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background()) |
|||
l1, err := Listen(ctx, p1.Addr, p1.ID, key1) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
d2 := &Dialer{ |
|||
LocalPeer: p2.ID, |
|||
PrivateKey: key2, |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
go echoListen(ctx, l1) |
|||
|
|||
c, err := d2.Dial(ctx, p1.Addr, p1.ID) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal("error dialing peer", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// fmt.Println("sending")
|
|||
c.WriteMsg([]byte("beep")) |
|||
c.WriteMsg([]byte("boop")) |
|||
|
|||
out, err := c.ReadMsg() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// fmt.Println("recving", string(out))
|
|||
data := string(out) |
|||
if data != "beep" { |
|||
t.Error("unexpected conn output", data) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
out, err = c.ReadMsg() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
data = string(out) |
|||
if string(out) != "boop" { |
|||
t.Error("unexpected conn output", data) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// fmt.Println("closing")
|
|||
c.Close() |
|||
l1.Close() |
|||
cancel() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestDialerInsecure(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
testDialer(t, false) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestDialerSecure(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
testDialer(t, true) |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,84 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package conn |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"io" |
|||
"net" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
u "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util" |
|||
|
|||
msgio "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-msgio" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// Map maps Keys (Peer.IDs) to Connections.
|
|||
type Map map[u.Key]Conn |
|||
|
|||
type PeerConn interface { |
|||
// LocalPeer (this side) ID, PrivateKey, and Address
|
|||
LocalPeer() peer.ID |
|||
LocalPrivateKey() ic.PrivKey |
|||
LocalMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr |
|||
|
|||
// RemotePeer ID, PublicKey, and Address
|
|||
RemotePeer() peer.ID |
|||
RemotePublicKey() ic.PubKey |
|||
RemoteMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Conn is a generic message-based Peer-to-Peer connection.
|
|||
type Conn interface { |
|||
PeerConn |
|||
|
|||
// ID is an identifier unique to this connection.
|
|||
ID() string |
|||
|
|||
// can't just say "net.Conn" cause we have duplicate methods.
|
|||
LocalAddr() net.Addr |
|||
RemoteAddr() net.Addr |
|||
SetDeadline(t time.Time) error |
|||
SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error |
|||
SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error |
|||
|
|||
msgio.Reader |
|||
msgio.Writer |
|||
io.Closer |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Dialer is an object that can open connections. We could have a "convenience"
|
|||
// Dial function as before, but it would have many arguments, as dialing is
|
|||
// no longer simple (need a peerstore, a local peer, a context, a network, etc)
|
|||
type Dialer struct { |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer is the identity of the local Peer.
|
|||
LocalPeer peer.ID |
|||
|
|||
// LocalAddrs is a set of local addresses to use.
|
|||
LocalAddrs []ma.Multiaddr |
|||
|
|||
// PrivateKey used to initialize a secure connection.
|
|||
// Warning: if PrivateKey is nil, connection will not be secured.
|
|||
PrivateKey ic.PrivKey |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Listener is an object that can accept connections. It matches net.Listener
|
|||
type Listener interface { |
|||
|
|||
// Accept waits for and returns the next connection to the listener.
|
|||
Accept() (net.Conn, error) |
|||
|
|||
// Addr is the local address
|
|||
Addr() net.Addr |
|||
|
|||
// Multiaddr is the local multiaddr address
|
|||
Multiaddr() ma.Multiaddr |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer is the identity of the local Peer.
|
|||
LocalPeer() peer.ID |
|||
|
|||
// Close closes the listener.
|
|||
// Any blocked Accept operations will be unblocked and return errors.
|
|||
Close() error |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,115 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package conn |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"net" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ctxgroup "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-ctxgroup" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
manet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr-net" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// listener is an object that can accept connections. It implements Listener
|
|||
type listener struct { |
|||
manet.Listener |
|||
|
|||
maddr ma.Multiaddr // Local multiaddr to listen on
|
|||
local peer.ID // LocalPeer is the identity of the local Peer
|
|||
privk ic.PrivKey // private key to use to initialize secure conns
|
|||
|
|||
cg ctxgroup.ContextGroup |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *listener) teardown() error { |
|||
defer log.Debugf("listener closed: %s %s", l.local, l.maddr) |
|||
return l.Listener.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *listener) Close() error { |
|||
log.Debugf("listener closing: %s %s", l.local, l.maddr) |
|||
return l.cg.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *listener) String() string { |
|||
return fmt.Sprintf("<Listener %s %s>", l.local, l.maddr) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Accept waits for and returns the next connection to the listener.
|
|||
// Note that unfortunately this
|
|||
func (l *listener) Accept() (net.Conn, error) { |
|||
|
|||
// listeners dont have contexts. given changes dont make sense here anymore
|
|||
// note that the parent of listener will Close, which will interrupt all io.
|
|||
// Contexts and io don't mix.
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
|
|||
maconn, err := l.Listener.Accept() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
c, err := newSingleConn(ctx, l.local, "", maconn) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Error accepting connection: %v", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if l.privk == nil { |
|||
log.Warning("listener %s listening INSECURELY!", l) |
|||
return c, nil |
|||
} |
|||
sc, err := newSecureConn(ctx, l.privk, c) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Error securing connection: %v", err) |
|||
} |
|||
return sc, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *listener) Addr() net.Addr { |
|||
return l.Listener.Addr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Multiaddr is the identity of the local Peer.
|
|||
func (l *listener) Multiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return l.maddr |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer is the identity of the local Peer.
|
|||
func (l *listener) LocalPeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return l.local |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *listener) Loggable() map[string]interface{} { |
|||
return map[string]interface{}{ |
|||
"listener": map[string]interface{}{ |
|||
"peer": l.LocalPeer(), |
|||
"address": l.Multiaddr(), |
|||
"secure": (l.privk != nil), |
|||
}, |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Listen listens on the particular multiaddr, with given peer and peerstore.
|
|||
func Listen(ctx context.Context, addr ma.Multiaddr, local peer.ID, sk ic.PrivKey) (Listener, error) { |
|||
|
|||
ml, err := manet.Listen(addr) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to listen on %s: %s", addr, err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
l := &listener{ |
|||
Listener: ml, |
|||
maddr: addr, |
|||
local: local, |
|||
privk: sk, |
|||
cg: ctxgroup.WithContext(ctx), |
|||
} |
|||
l.cg.SetTeardown(l.teardown) |
|||
|
|||
log.Infof("swarm listening on %s", l.Multiaddr()) |
|||
log.Event(ctx, "swarmListen", l) |
|||
return l, nil |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,154 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package conn |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"net" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
msgio "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-msgio" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
secio "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto/secio" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
errors "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/debugerror" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// secureConn wraps another Conn object with an encrypted channel.
|
|||
type secureConn struct { |
|||
|
|||
// the wrapped conn
|
|||
insecure Conn |
|||
|
|||
// secure io (wrapping insecure)
|
|||
secure msgio.ReadWriteCloser |
|||
|
|||
// secure Session
|
|||
session secio.Session |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// newConn constructs a new connection
|
|||
func newSecureConn(ctx context.Context, sk ic.PrivKey, insecure Conn) (Conn, error) { |
|||
|
|||
if insecure == nil { |
|||
return nil, errors.New("insecure is nil") |
|||
} |
|||
if insecure.LocalPeer() == "" { |
|||
return nil, errors.New("insecure.LocalPeer() is nil") |
|||
} |
|||
if sk == nil { |
|||
panic("way") |
|||
return nil, errors.New("private key is nil") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NewSession performs the secure handshake, which takes multiple RTT
|
|||
sessgen := secio.SessionGenerator{LocalID: insecure.LocalPeer(), PrivateKey: sk} |
|||
session, err := sessgen.NewSession(ctx, insecure) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
conn := &secureConn{ |
|||
insecure: insecure, |
|||
session: session, |
|||
secure: session.ReadWriter(), |
|||
} |
|||
log.Debugf("newSecureConn: %v to %v handshake success!", conn.LocalPeer(), conn.RemotePeer()) |
|||
return conn, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) Close() error { |
|||
if err := c.secure.Close(); err != nil { |
|||
c.insecure.Close() |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
return c.insecure.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ID is an identifier unique to this connection.
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) ID() string { |
|||
return ID(c) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) String() string { |
|||
return String(c, "secureConn") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) LocalAddr() net.Addr { |
|||
return c.insecure.LocalAddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) RemoteAddr() net.Addr { |
|||
return c.insecure.RemoteAddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) SetDeadline(t time.Time) error { |
|||
return c.insecure.SetDeadline(t) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error { |
|||
return c.insecure.SetReadDeadline(t) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error { |
|||
return c.insecure.SetWriteDeadline(t) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalMultiaddr is the Multiaddr on this side
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) LocalMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.insecure.LocalMultiaddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemoteMultiaddr is the Multiaddr on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) RemoteMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.insecure.RemoteMultiaddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer is the Peer on this side
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) LocalPeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.session.LocalPeer() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemotePeer is the Peer on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) RemotePeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.session.RemotePeer() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPrivateKey is the public key of the peer on this side
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) LocalPrivateKey() ic.PrivKey { |
|||
return c.session.LocalPrivateKey() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemotePubKey is the public key of the peer on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) RemotePublicKey() ic.PubKey { |
|||
return c.session.RemotePublicKey() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Read reads data, net.Conn style
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) Read(buf []byte) (int, error) { |
|||
return c.secure.Read(buf) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Write writes data, net.Conn style
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) Write(buf []byte) (int, error) { |
|||
return c.secure.Write(buf) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) NextMsgLen() (int, error) { |
|||
return c.secure.NextMsgLen() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ReadMsg reads data, net.Conn style
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) ReadMsg() ([]byte, error) { |
|||
return c.secure.ReadMsg() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// WriteMsg writes data, net.Conn style
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) WriteMsg(buf []byte) error { |
|||
return c.secure.WriteMsg(buf) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ReleaseMsg releases a buffer
|
|||
func (c *secureConn) ReleaseMsg(m []byte) { |
|||
c.secure.ReleaseMsg(m) |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,199 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package conn |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"bytes" |
|||
"os" |
|||
"runtime" |
|||
"sync" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
func upgradeToSecureConn(t *testing.T, ctx context.Context, sk ic.PrivKey, c Conn) (Conn, error) { |
|||
if c, ok := c.(*secureConn); ok { |
|||
return c, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// shouldn't happen, because dial + listen already return secure conns.
|
|||
s, err := newSecureConn(ctx, sk, c) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
return s, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func secureHandshake(t *testing.T, ctx context.Context, sk ic.PrivKey, c Conn, done chan error) { |
|||
_, err := upgradeToSecureConn(t, ctx, sk, c) |
|||
done <- err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestSecureSimple(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
|
|||
numMsgs := 100 |
|||
if testing.Short() { |
|||
numMsgs = 10 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
c1, c2, p1, p2 := setupSingleConn(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
done := make(chan error) |
|||
go secureHandshake(t, ctx, p1.PrivKey, c1, done) |
|||
go secureHandshake(t, ctx, p2.PrivKey, c2, done) |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < 2; i++ { |
|||
if err := <-done; err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < numMsgs; i++ { |
|||
testOneSendRecv(t, c1, c2) |
|||
testOneSendRecv(t, c2, c1) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
c1.Close() |
|||
c2.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestSecureClose(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
c1, c2, p1, p2 := setupSingleConn(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
done := make(chan error) |
|||
go secureHandshake(t, ctx, p1.PrivKey, c1, done) |
|||
go secureHandshake(t, ctx, p2.PrivKey, c2, done) |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < 2; i++ { |
|||
if err := <-done; err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
testOneSendRecv(t, c1, c2) |
|||
|
|||
c1.Close() |
|||
testNotOneSendRecv(t, c1, c2) |
|||
|
|||
c2.Close() |
|||
testNotOneSendRecv(t, c1, c2) |
|||
testNotOneSendRecv(t, c2, c1) |
|||
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestSecureCancelHandshake(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
|
|||
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background()) |
|||
c1, c2, p1, p2 := setupSingleConn(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
done := make(chan error) |
|||
go secureHandshake(t, ctx, p1.PrivKey, c1, done) |
|||
<-time.After(time.Millisecond) |
|||
cancel() // cancel ctx
|
|||
go secureHandshake(t, ctx, p2.PrivKey, c2, done) |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < 2; i++ { |
|||
if err := <-done; err == nil { |
|||
t.Error("cancel should've errored out") |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestSecureHandshakeFailsWithWrongKeys(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
|
|||
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background()) |
|||
defer cancel() |
|||
c1, c2, p1, p2 := setupSingleConn(t, ctx) |
|||
|
|||
done := make(chan error) |
|||
go secureHandshake(t, ctx, p2.PrivKey, c1, done) |
|||
go secureHandshake(t, ctx, p1.PrivKey, c2, done) |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < 2; i++ { |
|||
if err := <-done; err == nil { |
|||
t.Fatal("wrong keys should've errored out.") |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestSecureCloseLeak(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("Skipping in favor of another test")
|
|||
|
|||
if testing.Short() { |
|||
t.SkipNow() |
|||
} |
|||
if os.Getenv("TRAVIS") == "true" { |
|||
t.Skip("this doesn't work well on travis") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
runPair := func(c1, c2 Conn, num int) { |
|||
log.Debugf("runPair %d", num) |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < num; i++ { |
|||
log.Debugf("runPair iteration %d", i) |
|||
b1 := []byte("beep") |
|||
c1.WriteMsg(b1) |
|||
b2, err := c2.ReadMsg() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(b1, b2) { |
|||
panic("bytes not equal") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
b2 = []byte("beep") |
|||
c2.WriteMsg(b2) |
|||
b1, err = c1.ReadMsg() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(b1, b2) { |
|||
panic("bytes not equal") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
<-time.After(time.Microsecond * 5) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
var cons = 5 |
|||
var msgs = 50 |
|||
log.Debugf("Running %d connections * %d msgs.\n", cons, msgs) |
|||
|
|||
var wg sync.WaitGroup |
|||
for i := 0; i < cons; i++ { |
|||
wg.Add(1) |
|||
|
|||
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background()) |
|||
c1, c2, _, _ := setupSecureConn(t, ctx) |
|||
go func(c1, c2 Conn) { |
|||
|
|||
defer func() { |
|||
c1.Close() |
|||
c2.Close() |
|||
cancel() |
|||
wg.Done() |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
runPair(c1, c2, msgs) |
|||
}(c1, c2) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("Waiting...\n") |
|||
wg.Wait() |
|||
// done!
|
|||
|
|||
<-time.After(time.Millisecond * 150) |
|||
if runtime.NumGoroutine() > 20 { |
|||
// panic("uncomment me to debug")
|
|||
t.Fatal("leaking goroutines:", runtime.NumGoroutine()) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,133 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package net |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"io" |
|||
|
|||
conn "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2/conn" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ctxgroup "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-ctxgroup" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// MessageSizeMax is a soft (recommended) maximum for network messages.
|
|||
// One can write more, as the interface is a stream. But it is useful
|
|||
// to bunch it up into multiple read/writes when the whole message is
|
|||
// a single, large serialized object.
|
|||
const MessageSizeMax = 2 << 22 // 4MB
|
|||
|
|||
// Stream represents a bidirectional channel between two agents in
|
|||
// the IPFS network. "agent" is as granular as desired, potentially
|
|||
// being a "request -> reply" pair, or whole protocols.
|
|||
// Streams are backed by SPDY streams underneath the hood.
|
|||
type Stream interface { |
|||
io.Reader |
|||
io.Writer |
|||
io.Closer |
|||
|
|||
// Conn returns the connection this stream is part of.
|
|||
Conn() Conn |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// StreamHandler is the type of function used to listen for
|
|||
// streams opened by the remote side.
|
|||
type StreamHandler func(Stream) |
|||
|
|||
// Conn is a connection to a remote peer. It multiplexes streams.
|
|||
// Usually there is no need to use a Conn directly, but it may
|
|||
// be useful to get information about the peer on the other side:
|
|||
// stream.Conn().RemotePeer()
|
|||
type Conn interface { |
|||
conn.PeerConn |
|||
|
|||
// NewStream constructs a new Stream over this conn.
|
|||
NewStream() (Stream, error) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ConnHandler is the type of function used to listen for
|
|||
// connections opened by the remote side.
|
|||
type ConnHandler func(Conn) |
|||
|
|||
// Network is the interface used to connect to the outside world.
|
|||
// It dials and listens for connections. it uses a Swarm to pool
|
|||
// connnections (see swarm pkg, and peerstream.Swarm). Connections
|
|||
// are encrypted with a TLS-like protocol.
|
|||
type Network interface { |
|||
Dialer |
|||
io.Closer |
|||
|
|||
// SetStreamHandler sets the handler for new streams opened by the
|
|||
// remote side. This operation is threadsafe.
|
|||
SetStreamHandler(StreamHandler) |
|||
|
|||
// SetConnHandler sets the handler for new connections opened by the
|
|||
// remote side. This operation is threadsafe.
|
|||
SetConnHandler(ConnHandler) |
|||
|
|||
// NewStream returns a new stream to given peer p.
|
|||
// If there is no connection to p, attempts to create one.
|
|||
NewStream(peer.ID) (Stream, error) |
|||
|
|||
// ListenAddresses returns a list of addresses at which this network listens.
|
|||
ListenAddresses() []ma.Multiaddr |
|||
|
|||
// InterfaceListenAddresses returns a list of addresses at which this network
|
|||
// listens. It expands "any interface" addresses (/ip4/0.0.0.0, /ip6/::) to
|
|||
// use the known local interfaces.
|
|||
InterfaceListenAddresses() ([]ma.Multiaddr, error) |
|||
|
|||
// CtxGroup returns the network's contextGroup
|
|||
CtxGroup() ctxgroup.ContextGroup |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Dialer represents a service that can dial out to peers
|
|||
// (this is usually just a Network, but other services may not need the whole
|
|||
// stack, and thus it becomes easier to mock)
|
|||
type Dialer interface { |
|||
|
|||
// Peerstore returns the internal peerstore
|
|||
// This is useful to tell the dialer about a new address for a peer.
|
|||
// Or use one of the public keys found out over the network.
|
|||
Peerstore() peer.Peerstore |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer returns the local peer associated with this network
|
|||
LocalPeer() peer.ID |
|||
|
|||
// DialPeer establishes a connection to a given peer
|
|||
DialPeer(context.Context, peer.ID) (Conn, error) |
|||
|
|||
// ClosePeer closes the connection to a given peer
|
|||
ClosePeer(peer.ID) error |
|||
|
|||
// Connectedness returns a state signaling connection capabilities
|
|||
Connectedness(peer.ID) Connectedness |
|||
|
|||
// Peers returns the peers connected
|
|||
Peers() []peer.ID |
|||
|
|||
// Conns returns the connections in this Netowrk
|
|||
Conns() []Conn |
|||
|
|||
// ConnsToPeer returns the connections in this Netowrk for given peer.
|
|||
ConnsToPeer(p peer.ID) []Conn |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Connectedness signals the capacity for a connection with a given node.
|
|||
// It is used to signal to services and other peers whether a node is reachable.
|
|||
type Connectedness int |
|||
|
|||
const ( |
|||
// NotConnected means no connection to peer, and no extra information (default)
|
|||
NotConnected Connectedness = iota |
|||
|
|||
// Connected means has an open, live connection to peer
|
|||
Connected |
|||
|
|||
// CanConnect means recently connected to peer, terminated gracefully
|
|||
CanConnect |
|||
|
|||
// CannotConnect means recently attempted connecting but failed to connect.
|
|||
// (should signal "made effort, failed")
|
|||
CannotConnect |
|||
) |
|||
@ -1,101 +0,0 @@ |
|||
// Package mocknet provides a mock net.Network to test with.
|
|||
//
|
|||
// - a Mocknet has many inet.Networks
|
|||
// - a Mocknet has many Links
|
|||
// - a Link joins two inet.Networks
|
|||
// - inet.Conns and inet.Streams are created by inet.Networks
|
|||
package mocknet |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"io" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
host "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/host" |
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
|
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
type Mocknet interface { |
|||
|
|||
// GenPeer generates a peer and its inet.Network in the Mocknet
|
|||
GenPeer() (host.Host, error) |
|||
|
|||
// AddPeer adds an existing peer. we need both a privkey and addr.
|
|||
// ID is derived from PrivKey
|
|||
AddPeer(ic.PrivKey, ma.Multiaddr) (host.Host, error) |
|||
|
|||
// retrieve things (with randomized iteration order)
|
|||
Peers() []peer.ID |
|||
Net(peer.ID) inet.Network |
|||
Nets() []inet.Network |
|||
Host(peer.ID) host.Host |
|||
Hosts() []host.Host |
|||
Links() LinkMap |
|||
LinksBetweenPeers(a, b peer.ID) []Link |
|||
LinksBetweenNets(a, b inet.Network) []Link |
|||
|
|||
// Links are the **ability to connect**.
|
|||
// think of Links as the physical medium.
|
|||
// For p1 and p2 to connect, a link must exist between them.
|
|||
// (this makes it possible to test dial failures, and
|
|||
// things like relaying traffic)
|
|||
LinkPeers(peer.ID, peer.ID) (Link, error) |
|||
LinkNets(inet.Network, inet.Network) (Link, error) |
|||
Unlink(Link) error |
|||
UnlinkPeers(peer.ID, peer.ID) error |
|||
UnlinkNets(inet.Network, inet.Network) error |
|||
|
|||
// LinkDefaults are the default options that govern links
|
|||
// if they do not have thier own option set.
|
|||
SetLinkDefaults(LinkOptions) |
|||
LinkDefaults() LinkOptions |
|||
|
|||
// Connections are the usual. Connecting means Dialing.
|
|||
// **to succeed, peers must be linked beforehand**
|
|||
ConnectPeers(peer.ID, peer.ID) (inet.Conn, error) |
|||
ConnectNets(inet.Network, inet.Network) (inet.Conn, error) |
|||
DisconnectPeers(peer.ID, peer.ID) error |
|||
DisconnectNets(inet.Network, inet.Network) error |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LinkOptions are used to change aspects of the links.
|
|||
// Sorry but they dont work yet :(
|
|||
type LinkOptions struct { |
|||
Latency time.Duration |
|||
Bandwidth int // in bytes-per-second
|
|||
// we can make these values distributions down the road.
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Link represents the **possibility** of a connection between
|
|||
// two peers. Think of it like physical network links. Without
|
|||
// them, the peers can try and try but they won't be able to
|
|||
// connect. This allows constructing topologies where specific
|
|||
// nodes cannot talk to each other directly. :)
|
|||
type Link interface { |
|||
Networks() []inet.Network |
|||
Peers() []peer.ID |
|||
|
|||
SetOptions(LinkOptions) |
|||
Options() LinkOptions |
|||
|
|||
// Metrics() Metrics
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LinkMap is a 3D map to give us an easy way to track links.
|
|||
// (wow, much map. so data structure. how compose. ahhh pointer)
|
|||
type LinkMap map[string]map[string]map[Link]struct{} |
|||
|
|||
// Printer lets you inspect things :)
|
|||
type Printer interface { |
|||
// MocknetLinks shows the entire Mocknet's link table :)
|
|||
MocknetLinks(mn Mocknet) |
|||
NetworkConns(ni inet.Network) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// PrinterTo returns a Printer ready to write to w.
|
|||
func PrinterTo(w io.Writer) Printer { |
|||
return &printer{w} |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,63 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mocknet |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = eventlog.Logger("mocknet") |
|||
|
|||
// WithNPeers constructs a Mocknet with N peers.
|
|||
func WithNPeers(ctx context.Context, n int) (Mocknet, error) { |
|||
m := New(ctx) |
|||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ { |
|||
if _, err := m.GenPeer(); err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return m, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// FullMeshLinked constructs a Mocknet with full mesh of Links.
|
|||
// This means that all the peers **can** connect to each other
|
|||
// (not that they already are connected. you can use m.ConnectAll())
|
|||
func FullMeshLinked(ctx context.Context, n int) (Mocknet, error) { |
|||
m, err := WithNPeers(ctx, n) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
nets := m.Nets() |
|||
for _, n1 := range nets { |
|||
for _, n2 := range nets { |
|||
// yes, even self.
|
|||
if _, err := m.LinkNets(n1, n2); err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return m, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// FullMeshConnected constructs a Mocknet with full mesh of Connections.
|
|||
// This means that all the peers have dialed and are ready to talk to
|
|||
// each other.
|
|||
func FullMeshConnected(ctx context.Context, n int) (Mocknet, error) { |
|||
m, err := FullMeshLinked(ctx, n) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
nets := m.Nets() |
|||
for _, n1 := range nets { |
|||
for _, n2 := range nets { |
|||
if _, err := m.ConnectNets(n1, n2); err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return m, nil |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,120 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mocknet |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"container/list" |
|||
"sync" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
|
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// conn represents one side's perspective of a
|
|||
// live connection between two peers.
|
|||
// it goes over a particular link.
|
|||
type conn struct { |
|||
local peer.ID |
|||
remote peer.ID |
|||
|
|||
localAddr ma.Multiaddr |
|||
remoteAddr ma.Multiaddr |
|||
|
|||
localPrivKey ic.PrivKey |
|||
remotePubKey ic.PubKey |
|||
|
|||
net *peernet |
|||
link *link |
|||
rconn *conn // counterpart
|
|||
streams list.List |
|||
|
|||
sync.RWMutex |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn) Close() error { |
|||
for _, s := range c.allStreams() { |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
c.net.removeConn(c) |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn) addStream(s *stream) { |
|||
c.Lock() |
|||
s.conn = c |
|||
c.streams.PushBack(s) |
|||
c.Unlock() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn) removeStream(s *stream) { |
|||
c.Lock() |
|||
defer c.Unlock() |
|||
for e := c.streams.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next() { |
|||
if s == e.Value { |
|||
c.streams.Remove(e) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn) allStreams() []inet.Stream { |
|||
c.RLock() |
|||
defer c.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
strs := make([]inet.Stream, 0, c.streams.Len()) |
|||
for e := c.streams.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next() { |
|||
s := e.Value.(*stream) |
|||
strs = append(strs, s) |
|||
} |
|||
return strs |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn) remoteOpenedStream(s *stream) { |
|||
c.addStream(s) |
|||
c.net.handleNewStream(s) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn) openStream() *stream { |
|||
sl, sr := c.link.newStreamPair() |
|||
c.addStream(sl) |
|||
c.rconn.remoteOpenedStream(sr) |
|||
return sl |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *conn) NewStream() (inet.Stream, error) { |
|||
log.Debugf("Conn.NewStreamWithProtocol: %s --> %s", c.local, c.remote) |
|||
|
|||
s := c.openStream() |
|||
return s, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalMultiaddr is the Multiaddr on this side
|
|||
func (c *conn) LocalMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.localAddr |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer is the Peer on our side of the connection
|
|||
func (c *conn) LocalPeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.local |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPrivateKey is the private key of the peer on our side.
|
|||
func (c *conn) LocalPrivateKey() ic.PrivKey { |
|||
return c.localPrivKey |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemoteMultiaddr is the Multiaddr on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *conn) RemoteMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.remoteAddr |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemotePeer is the Peer on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *conn) RemotePeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.remote |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemotePublicKey is the private key of the peer on our side.
|
|||
func (c *conn) RemotePublicKey() ic.PubKey { |
|||
return c.remotePubKey |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,93 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mocknet |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"io" |
|||
"sync" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// link implements mocknet.Link
|
|||
// and, for simplicity, inet.Conn
|
|||
type link struct { |
|||
mock *mocknet |
|||
nets []*peernet |
|||
opts LinkOptions |
|||
|
|||
// this could have addresses on both sides.
|
|||
|
|||
sync.RWMutex |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func newLink(mn *mocknet, opts LinkOptions) *link { |
|||
return &link{mock: mn, opts: opts} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *link) newConnPair(dialer *peernet) (*conn, *conn) { |
|||
l.RLock() |
|||
defer l.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
mkconn := func(ln, rn *peernet) *conn { |
|||
c := &conn{net: ln, link: l} |
|||
c.local = ln.peer |
|||
c.remote = rn.peer |
|||
|
|||
c.localAddr = ln.ps.Addresses(ln.peer)[0] |
|||
c.remoteAddr = rn.ps.Addresses(rn.peer)[0] |
|||
|
|||
c.localPrivKey = ln.ps.PrivKey(ln.peer) |
|||
c.remotePubKey = rn.ps.PubKey(rn.peer) |
|||
|
|||
return c |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
c1 := mkconn(l.nets[0], l.nets[1]) |
|||
c2 := mkconn(l.nets[1], l.nets[0]) |
|||
c1.rconn = c2 |
|||
c2.rconn = c1 |
|||
|
|||
if dialer == c1.net { |
|||
return c1, c2 |
|||
} |
|||
return c2, c1 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *link) newStreamPair() (*stream, *stream) { |
|||
r1, w1 := io.Pipe() |
|||
r2, w2 := io.Pipe() |
|||
|
|||
s1 := &stream{Reader: r1, Writer: w2} |
|||
s2 := &stream{Reader: r2, Writer: w1} |
|||
return s1, s2 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *link) Networks() []inet.Network { |
|||
l.RLock() |
|||
defer l.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
cp := make([]inet.Network, len(l.nets)) |
|||
for i, n := range l.nets { |
|||
cp[i] = n |
|||
} |
|||
return cp |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *link) Peers() []peer.ID { |
|||
l.RLock() |
|||
defer l.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
cp := make([]peer.ID, len(l.nets)) |
|||
for i, n := range l.nets { |
|||
cp[i] = n.peer |
|||
} |
|||
return cp |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *link) SetOptions(o LinkOptions) { |
|||
l.opts = o |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (l *link) Options() LinkOptions { |
|||
return l.opts |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,340 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mocknet |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"sync" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
host "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/host" |
|||
bhost "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/host/basic" |
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
testutil "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/testutil" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ctxgroup "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-ctxgroup" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// mocknet implements mocknet.Mocknet
|
|||
type mocknet struct { |
|||
nets map[peer.ID]*peernet |
|||
hosts map[peer.ID]*bhost.BasicHost |
|||
|
|||
// links make it possible to connect two peers.
|
|||
// think of links as the physical medium.
|
|||
// usually only one, but there could be multiple
|
|||
// **links are shared between peers**
|
|||
links map[peer.ID]map[peer.ID]map[*link]struct{} |
|||
|
|||
linkDefaults LinkOptions |
|||
|
|||
cg ctxgroup.ContextGroup // for Context closing
|
|||
sync.RWMutex |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func New(ctx context.Context) Mocknet { |
|||
return &mocknet{ |
|||
nets: map[peer.ID]*peernet{}, |
|||
hosts: map[peer.ID]*bhost.BasicHost{}, |
|||
links: map[peer.ID]map[peer.ID]map[*link]struct{}{}, |
|||
cg: ctxgroup.WithContext(ctx), |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) GenPeer() (host.Host, error) { |
|||
sk, _, err := testutil.RandKeyPair(512) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
a := testutil.RandLocalTCPAddress() |
|||
|
|||
h, err := mn.AddPeer(sk, a) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return h, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) AddPeer(k ic.PrivKey, a ma.Multiaddr) (host.Host, error) { |
|||
n, err := newPeernet(mn.cg.Context(), mn, k, a) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
h := bhost.New(n) |
|||
|
|||
// make sure to add listening address!
|
|||
// this makes debugging things simpler as remembering to register
|
|||
// an address may cause unexpected failure.
|
|||
n.Peerstore().AddAddress(n.LocalPeer(), a) |
|||
log.Debugf("mocknet added listen addr for peer: %s -- %s", n.LocalPeer(), a) |
|||
|
|||
mn.cg.AddChildGroup(n.cg) |
|||
|
|||
mn.Lock() |
|||
mn.nets[n.peer] = n |
|||
mn.hosts[n.peer] = h |
|||
mn.Unlock() |
|||
return h, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) Peers() []peer.ID { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
defer mn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
cp := make([]peer.ID, 0, len(mn.nets)) |
|||
for _, n := range mn.nets { |
|||
cp = append(cp, n.peer) |
|||
} |
|||
return cp |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) Host(pid peer.ID) host.Host { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
host := mn.hosts[pid] |
|||
mn.RUnlock() |
|||
return host |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) Net(pid peer.ID) inet.Network { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
n := mn.nets[pid] |
|||
mn.RUnlock() |
|||
return n |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) Hosts() []host.Host { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
defer mn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
cp := make([]host.Host, 0, len(mn.hosts)) |
|||
for _, h := range mn.hosts { |
|||
cp = append(cp, h) |
|||
} |
|||
return cp |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) Nets() []inet.Network { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
defer mn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
cp := make([]inet.Network, 0, len(mn.nets)) |
|||
for _, n := range mn.nets { |
|||
cp = append(cp, n) |
|||
} |
|||
return cp |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Links returns a copy of the internal link state map.
|
|||
// (wow, much map. so data structure. how compose. ahhh pointer)
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) Links() LinkMap { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
defer mn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
links := map[string]map[string]map[Link]struct{}{} |
|||
for p1, lm := range mn.links { |
|||
sp1 := string(p1) |
|||
links[sp1] = map[string]map[Link]struct{}{} |
|||
for p2, ls := range lm { |
|||
sp2 := string(p2) |
|||
links[sp1][sp2] = map[Link]struct{}{} |
|||
for l := range ls { |
|||
links[sp1][sp2][l] = struct{}{} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return links |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) LinkAll() error { |
|||
nets := mn.Nets() |
|||
for _, n1 := range nets { |
|||
for _, n2 := range nets { |
|||
if _, err := mn.LinkNets(n1, n2); err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) LinkPeers(p1, p2 peer.ID) (Link, error) { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
n1 := mn.nets[p1] |
|||
n2 := mn.nets[p2] |
|||
mn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
if n1 == nil { |
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("network for p1 not in mocknet") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if n2 == nil { |
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("network for p2 not in mocknet") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return mn.LinkNets(n1, n2) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) validate(n inet.Network) (*peernet, error) { |
|||
// WARNING: assumes locks acquired
|
|||
|
|||
nr, ok := n.(*peernet) |
|||
if !ok { |
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Network not supported (use mock package nets only)") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if _, found := mn.nets[nr.peer]; !found { |
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Network not on mocknet. is it from another mocknet?") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return nr, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) LinkNets(n1, n2 inet.Network) (Link, error) { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
n1r, err1 := mn.validate(n1) |
|||
n2r, err2 := mn.validate(n2) |
|||
ld := mn.linkDefaults |
|||
mn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
if err1 != nil { |
|||
return nil, err1 |
|||
} |
|||
if err2 != nil { |
|||
return nil, err2 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
l := newLink(mn, ld) |
|||
l.nets = append(l.nets, n1r, n2r) |
|||
mn.addLink(l) |
|||
return l, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) Unlink(l2 Link) error { |
|||
|
|||
l, ok := l2.(*link) |
|||
if !ok { |
|||
return fmt.Errorf("only links from mocknet are supported") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
mn.removeLink(l) |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) UnlinkPeers(p1, p2 peer.ID) error { |
|||
ls := mn.LinksBetweenPeers(p1, p2) |
|||
if ls == nil { |
|||
return fmt.Errorf("no link between p1 and p2") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for _, l := range ls { |
|||
if err := mn.Unlink(l); err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) UnlinkNets(n1, n2 inet.Network) error { |
|||
return mn.UnlinkPeers(n1.LocalPeer(), n2.LocalPeer()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// get from the links map. and lazily contruct.
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) linksMapGet(p1, p2 peer.ID) *map[*link]struct{} { |
|||
|
|||
l1, found := mn.links[p1] |
|||
if !found { |
|||
mn.links[p1] = map[peer.ID]map[*link]struct{}{} |
|||
l1 = mn.links[p1] // so we make sure it's there.
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
l2, found := l1[p2] |
|||
if !found { |
|||
m := map[*link]struct{}{} |
|||
l1[p2] = m |
|||
l2 = l1[p2] |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return &l2 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) addLink(l *link) { |
|||
mn.Lock() |
|||
defer mn.Unlock() |
|||
|
|||
n1, n2 := l.nets[0], l.nets[1] |
|||
(*mn.linksMapGet(n1.peer, n2.peer))[l] = struct{}{} |
|||
(*mn.linksMapGet(n2.peer, n1.peer))[l] = struct{}{} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) removeLink(l *link) { |
|||
mn.Lock() |
|||
defer mn.Unlock() |
|||
|
|||
n1, n2 := l.nets[0], l.nets[1] |
|||
delete(*mn.linksMapGet(n1.peer, n2.peer), l) |
|||
delete(*mn.linksMapGet(n2.peer, n1.peer), l) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) ConnectAll() error { |
|||
nets := mn.Nets() |
|||
for _, n1 := range nets { |
|||
for _, n2 := range nets { |
|||
if n1 == n2 { |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if _, err := mn.ConnectNets(n1, n2); err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) ConnectPeers(a, b peer.ID) (inet.Conn, error) { |
|||
return mn.Net(a).DialPeer(mn.cg.Context(), b) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) ConnectNets(a, b inet.Network) (inet.Conn, error) { |
|||
return a.DialPeer(mn.cg.Context(), b.LocalPeer()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) DisconnectPeers(p1, p2 peer.ID) error { |
|||
return mn.Net(p1).ClosePeer(p2) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) DisconnectNets(n1, n2 inet.Network) error { |
|||
return n1.ClosePeer(n2.LocalPeer()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) LinksBetweenPeers(p1, p2 peer.ID) []Link { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
defer mn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
ls2 := *mn.linksMapGet(p1, p2) |
|||
cp := make([]Link, 0, len(ls2)) |
|||
for l := range ls2 { |
|||
cp = append(cp, l) |
|||
} |
|||
return cp |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) LinksBetweenNets(n1, n2 inet.Network) []Link { |
|||
return mn.LinksBetweenPeers(n1.LocalPeer(), n2.LocalPeer()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) SetLinkDefaults(o LinkOptions) { |
|||
mn.Lock() |
|||
mn.linkDefaults = o |
|||
mn.Unlock() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (mn *mocknet) LinkDefaults() LinkOptions { |
|||
mn.RLock() |
|||
defer mn.RUnlock() |
|||
return mn.linkDefaults |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,353 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mocknet |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"math/rand" |
|||
"sync" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ctxgroup "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-ctxgroup" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// peernet implements inet.Network
|
|||
type peernet struct { |
|||
mocknet *mocknet // parent
|
|||
|
|||
peer peer.ID |
|||
ps peer.Peerstore |
|||
|
|||
// conns are actual live connections between peers.
|
|||
// many conns could run over each link.
|
|||
// **conns are NOT shared between peers**
|
|||
connsByPeer map[peer.ID]map[*conn]struct{} |
|||
connsByLink map[*link]map[*conn]struct{} |
|||
|
|||
// implement inet.Network
|
|||
streamHandler inet.StreamHandler |
|||
connHandler inet.ConnHandler |
|||
|
|||
cg ctxgroup.ContextGroup |
|||
sync.RWMutex |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// newPeernet constructs a new peernet
|
|||
func newPeernet(ctx context.Context, m *mocknet, k ic.PrivKey, |
|||
a ma.Multiaddr) (*peernet, error) { |
|||
|
|||
p, err := peer.IDFromPublicKey(k.GetPublic()) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// create our own entirely, so that peers knowledge doesn't get shared
|
|||
ps := peer.NewPeerstore() |
|||
ps.AddAddress(p, a) |
|||
ps.AddPrivKey(p, k) |
|||
ps.AddPubKey(p, k.GetPublic()) |
|||
|
|||
n := &peernet{ |
|||
mocknet: m, |
|||
peer: p, |
|||
ps: ps, |
|||
cg: ctxgroup.WithContext(ctx), |
|||
|
|||
connsByPeer: map[peer.ID]map[*conn]struct{}{}, |
|||
connsByLink: map[*link]map[*conn]struct{}{}, |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
n.cg.SetTeardown(n.teardown) |
|||
return n, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) teardown() error { |
|||
|
|||
// close the connections
|
|||
for _, c := range pn.allConns() { |
|||
c.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// allConns returns all the connections between this peer and others
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) allConns() []*conn { |
|||
pn.RLock() |
|||
var cs []*conn |
|||
for _, csl := range pn.connsByPeer { |
|||
for c := range csl { |
|||
cs = append(cs, c) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
pn.RUnlock() |
|||
return cs |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Close calls the ContextCloser func
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) Close() error { |
|||
return pn.cg.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) Peerstore() peer.Peerstore { |
|||
return pn.ps |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) String() string { |
|||
return fmt.Sprintf("<mock.peernet %s - %d conns>", pn.peer, len(pn.allConns())) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// handleNewStream is an internal function to trigger the client's handler
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) handleNewStream(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
pn.RLock() |
|||
handler := pn.streamHandler |
|||
pn.RUnlock() |
|||
if handler != nil { |
|||
go handler(s) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// handleNewConn is an internal function to trigger the client's handler
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) handleNewConn(c inet.Conn) { |
|||
pn.RLock() |
|||
handler := pn.connHandler |
|||
pn.RUnlock() |
|||
if handler != nil { |
|||
go handler(c) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// DialPeer attempts to establish a connection to a given peer.
|
|||
// Respects the context.
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) DialPeer(ctx context.Context, p peer.ID) (inet.Conn, error) { |
|||
return pn.connect(p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) connect(p peer.ID) (*conn, error) { |
|||
// first, check if we already have live connections
|
|||
pn.RLock() |
|||
cs, found := pn.connsByPeer[p] |
|||
pn.RUnlock() |
|||
if found && len(cs) > 0 { |
|||
for c := range cs { |
|||
return c, nil |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s (newly) dialing %s", pn.peer, p) |
|||
|
|||
// ok, must create a new connection. we need a link
|
|||
links := pn.mocknet.LinksBetweenPeers(pn.peer, p) |
|||
if len(links) < 1 { |
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("%s cannot connect to %s", pn.peer, p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// if many links found, how do we select? for now, randomly...
|
|||
// this would be an interesting place to test logic that can measure
|
|||
// links (network interfaces) and select properly
|
|||
l := links[rand.Intn(len(links))] |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s dialing %s openingConn", pn.peer, p) |
|||
// create a new connection with link
|
|||
c := pn.openConn(p, l.(*link)) |
|||
return c, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) openConn(r peer.ID, l *link) *conn { |
|||
lc, rc := l.newConnPair(pn) |
|||
log.Debugf("%s opening connection to %s", pn.LocalPeer(), lc.RemotePeer()) |
|||
pn.addConn(lc) |
|||
rc.net.remoteOpenedConn(rc) |
|||
return lc |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) remoteOpenedConn(c *conn) { |
|||
log.Debugf("%s accepting connection from %s", pn.LocalPeer(), c.RemotePeer()) |
|||
pn.addConn(c) |
|||
pn.handleNewConn(c) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// addConn constructs and adds a connection
|
|||
// to given remote peer over given link
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) addConn(c *conn) { |
|||
pn.Lock() |
|||
defer pn.Unlock() |
|||
|
|||
cs, found := pn.connsByPeer[c.RemotePeer()] |
|||
if !found { |
|||
cs = map[*conn]struct{}{} |
|||
pn.connsByPeer[c.RemotePeer()] = cs |
|||
} |
|||
pn.connsByPeer[c.RemotePeer()][c] = struct{}{} |
|||
|
|||
cs, found = pn.connsByLink[c.link] |
|||
if !found { |
|||
cs = map[*conn]struct{}{} |
|||
pn.connsByLink[c.link] = cs |
|||
} |
|||
pn.connsByLink[c.link][c] = struct{}{} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// removeConn removes a given conn
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) removeConn(c *conn) { |
|||
pn.Lock() |
|||
defer pn.Unlock() |
|||
|
|||
cs, found := pn.connsByLink[c.link] |
|||
if !found || len(cs) < 1 { |
|||
panic("attempting to remove a conn that doesnt exist") |
|||
} |
|||
delete(cs, c) |
|||
|
|||
cs, found = pn.connsByPeer[c.remote] |
|||
if !found { |
|||
panic("attempting to remove a conn that doesnt exist") |
|||
} |
|||
delete(cs, c) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// CtxGroup returns the network's ContextGroup
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) CtxGroup() ctxgroup.ContextGroup { |
|||
return pn.cg |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer the network's LocalPeer
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) LocalPeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return pn.peer |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Peers returns the connected peers
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) Peers() []peer.ID { |
|||
pn.RLock() |
|||
defer pn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
peers := make([]peer.ID, 0, len(pn.connsByPeer)) |
|||
for _, cs := range pn.connsByPeer { |
|||
for c := range cs { |
|||
peers = append(peers, c.remote) |
|||
break |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return peers |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Conns returns all the connections of this peer
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) Conns() []inet.Conn { |
|||
pn.RLock() |
|||
defer pn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
out := make([]inet.Conn, 0, len(pn.connsByPeer)) |
|||
for _, cs := range pn.connsByPeer { |
|||
for c := range cs { |
|||
out = append(out, c) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return out |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) ConnsToPeer(p peer.ID) []inet.Conn { |
|||
pn.RLock() |
|||
defer pn.RUnlock() |
|||
|
|||
cs, found := pn.connsByPeer[p] |
|||
if !found || len(cs) == 0 { |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
var cs2 []inet.Conn |
|||
for c := range cs { |
|||
cs2 = append(cs2, c) |
|||
} |
|||
return cs2 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ClosePeer connections to peer
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) ClosePeer(p peer.ID) error { |
|||
pn.RLock() |
|||
cs, found := pn.connsByPeer[p] |
|||
pn.RUnlock() |
|||
if !found { |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for c := range cs { |
|||
c.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// BandwidthTotals returns the total amount of bandwidth transferred
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) BandwidthTotals() (in uint64, out uint64) { |
|||
// need to implement this. probably best to do it in swarm this time.
|
|||
// need a "metrics" object
|
|||
return 0, 0 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ListenAddresses returns a list of addresses at which this network listens.
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) ListenAddresses() []ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return pn.Peerstore().Addresses(pn.LocalPeer()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// InterfaceListenAddresses returns a list of addresses at which this network
|
|||
// listens. It expands "any interface" addresses (/ip4/0.0.0.0, /ip6/::) to
|
|||
// use the known local interfaces.
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) InterfaceListenAddresses() ([]ma.Multiaddr, error) { |
|||
return pn.ListenAddresses(), nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Connectedness returns a state signaling connection capabilities
|
|||
// For now only returns Connecter || NotConnected. Expand into more later.
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) Connectedness(p peer.ID) inet.Connectedness { |
|||
pn.Lock() |
|||
defer pn.Unlock() |
|||
|
|||
cs, found := pn.connsByPeer[p] |
|||
if found && len(cs) > 0 { |
|||
return inet.Connected |
|||
} |
|||
return inet.NotConnected |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NewStream returns a new stream to given peer p.
|
|||
// If there is no connection to p, attempts to create one.
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) NewStream(p peer.ID) (inet.Stream, error) { |
|||
pn.Lock() |
|||
cs, found := pn.connsByPeer[p] |
|||
if !found || len(cs) < 1 { |
|||
pn.Unlock() |
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("no connection to peer") |
|||
} |
|||
pn.Unlock() |
|||
|
|||
// if many conns are found, how do we select? for now, randomly...
|
|||
// this would be an interesting place to test logic that can measure
|
|||
// links (network interfaces) and select properly
|
|||
n := rand.Intn(len(cs)) |
|||
var c *conn |
|||
for c = range cs { |
|||
if n == 0 { |
|||
break |
|||
} |
|||
n-- |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return c.NewStream() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// SetStreamHandler sets the new stream handler on the Network.
|
|||
// This operation is threadsafe.
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) SetStreamHandler(h inet.StreamHandler) { |
|||
pn.Lock() |
|||
pn.streamHandler = h |
|||
pn.Unlock() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// SetConnHandler sets the new conn handler on the Network.
|
|||
// This operation is threadsafe.
|
|||
func (pn *peernet) SetConnHandler(h inet.ConnHandler) { |
|||
pn.Lock() |
|||
pn.connHandler = h |
|||
pn.Unlock() |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mocknet |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
"io" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// separate object so our interfaces are separate :)
|
|||
type printer struct { |
|||
w io.Writer |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (p *printer) MocknetLinks(mn Mocknet) { |
|||
links := mn.Links() |
|||
|
|||
fmt.Fprintf(p.w, "Mocknet link map:\n") |
|||
for p1, lm := range links { |
|||
fmt.Fprintf(p.w, "\t%s linked to:\n", peer.ID(p1)) |
|||
for p2, l := range lm { |
|||
fmt.Fprintf(p.w, "\t\t%s (%d links)\n", peer.ID(p2), len(l)) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
fmt.Fprintf(p.w, "\n") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (p *printer) NetworkConns(ni inet.Network) { |
|||
|
|||
fmt.Fprintf(p.w, "%s connected to:\n", ni.LocalPeer()) |
|||
for _, c := range ni.Conns() { |
|||
fmt.Fprintf(p.w, "\t%s (addr: %s)\n", c.RemotePeer(), c.RemoteMultiaddr()) |
|||
} |
|||
fmt.Fprintf(p.w, "\n") |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,29 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mocknet |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"io" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// stream implements inet.Stream
|
|||
type stream struct { |
|||
io.Reader |
|||
io.Writer |
|||
conn *conn |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (s *stream) Close() error { |
|||
s.conn.removeStream(s) |
|||
if r, ok := (s.Reader).(io.Closer); ok { |
|||
r.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
if w, ok := (s.Writer).(io.Closer); ok { |
|||
return w.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (s *stream) Conn() inet.Conn { |
|||
return s.conn |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,475 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package mocknet |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"bytes" |
|||
"io" |
|||
"math/rand" |
|||
"sync" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
protocol "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/protocol" |
|||
testutil "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/testutil" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
func randPeer(t *testing.T) peer.ID { |
|||
p, err := testutil.RandPeerID() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
return p |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestNetworkSetup(t *testing.T) { |
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
sk1, _, err := testutil.RandKeyPair(512) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(t) |
|||
} |
|||
sk2, _, err := testutil.RandKeyPair(512) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(t) |
|||
} |
|||
sk3, _, err := testutil.RandKeyPair(512) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(t) |
|||
} |
|||
mn := New(ctx) |
|||
// peers := []peer.ID{p1, p2, p3}
|
|||
|
|||
// add peers to mock net
|
|||
|
|||
a1 := testutil.RandLocalTCPAddress() |
|||
a2 := testutil.RandLocalTCPAddress() |
|||
a3 := testutil.RandLocalTCPAddress() |
|||
|
|||
h1, err := mn.AddPeer(sk1, a1) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
p1 := h1.ID() |
|||
|
|||
h2, err := mn.AddPeer(sk2, a2) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
p2 := h2.ID() |
|||
|
|||
h3, err := mn.AddPeer(sk3, a3) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
p3 := h3.ID() |
|||
|
|||
// check peers and net
|
|||
if mn.Host(p1) != h1 { |
|||
t.Error("host for p1.ID != h1") |
|||
} |
|||
if mn.Host(p2) != h2 { |
|||
t.Error("host for p2.ID != h2") |
|||
} |
|||
if mn.Host(p3) != h3 { |
|||
t.Error("host for p3.ID != h3") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
n1 := h1.Network() |
|||
if mn.Net(p1) != n1 { |
|||
t.Error("net for p1.ID != n1") |
|||
} |
|||
n2 := h2.Network() |
|||
if mn.Net(p2) != n2 { |
|||
t.Error("net for p2.ID != n1") |
|||
} |
|||
n3 := h3.Network() |
|||
if mn.Net(p3) != n3 { |
|||
t.Error("net for p3.ID != n1") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// link p1<-->p2, p1<-->p1, p2<-->p3, p3<-->p2
|
|||
|
|||
l12, err := mn.LinkPeers(p1, p2) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !(l12.Networks()[0] == n1 && l12.Networks()[1] == n2) && |
|||
!(l12.Networks()[0] == n2 && l12.Networks()[1] == n1) { |
|||
t.Error("l12 networks incorrect") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
l11, err := mn.LinkPeers(p1, p1) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !(l11.Networks()[0] == n1 && l11.Networks()[1] == n1) { |
|||
t.Error("l11 networks incorrect") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
l23, err := mn.LinkPeers(p2, p3) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !(l23.Networks()[0] == n2 && l23.Networks()[1] == n3) && |
|||
!(l23.Networks()[0] == n3 && l23.Networks()[1] == n2) { |
|||
t.Error("l23 networks incorrect") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
l32, err := mn.LinkPeers(p3, p2) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !(l32.Networks()[0] == n2 && l32.Networks()[1] == n3) && |
|||
!(l32.Networks()[0] == n3 && l32.Networks()[1] == n2) { |
|||
t.Error("l32 networks incorrect") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// check things
|
|||
|
|||
links12 := mn.LinksBetweenPeers(p1, p2) |
|||
if len(links12) != 1 { |
|||
t.Errorf("should be 1 link bt. p1 and p2 (found %d)", len(links12)) |
|||
} |
|||
if links12[0] != l12 { |
|||
t.Error("links 1-2 should be l12.") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
links11 := mn.LinksBetweenPeers(p1, p1) |
|||
if len(links11) != 1 { |
|||
t.Errorf("should be 1 link bt. p1 and p1 (found %d)", len(links11)) |
|||
} |
|||
if links11[0] != l11 { |
|||
t.Error("links 1-1 should be l11.") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
links23 := mn.LinksBetweenPeers(p2, p3) |
|||
if len(links23) != 2 { |
|||
t.Errorf("should be 2 link bt. p2 and p3 (found %d)", len(links23)) |
|||
} |
|||
if !((links23[0] == l23 && links23[1] == l32) || |
|||
(links23[0] == l32 && links23[1] == l23)) { |
|||
t.Error("links 2-3 should be l23 and l32.") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// unlinking
|
|||
|
|||
if err := mn.UnlinkPeers(p2, p1); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// check only one link affected:
|
|||
|
|||
links12 = mn.LinksBetweenPeers(p1, p2) |
|||
if len(links12) != 0 { |
|||
t.Errorf("should be 0 now...", len(links12)) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
links11 = mn.LinksBetweenPeers(p1, p1) |
|||
if len(links11) != 1 { |
|||
t.Errorf("should be 1 link bt. p1 and p1 (found %d)", len(links11)) |
|||
} |
|||
if links11[0] != l11 { |
|||
t.Error("links 1-1 should be l11.") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
links23 = mn.LinksBetweenPeers(p2, p3) |
|||
if len(links23) != 2 { |
|||
t.Errorf("should be 2 link bt. p2 and p3 (found %d)", len(links23)) |
|||
} |
|||
if !((links23[0] == l23 && links23[1] == l32) || |
|||
(links23[0] == l32 && links23[1] == l23)) { |
|||
t.Error("links 2-3 should be l23 and l32.") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// check connecting
|
|||
|
|||
// first, no conns
|
|||
if len(n2.Conns()) > 0 || len(n3.Conns()) > 0 { |
|||
t.Error("should have 0 conn. Got: (%d, %d)", len(n2.Conns()), len(n3.Conns())) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// connect p2->p3
|
|||
if _, err := n2.DialPeer(ctx, p3); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if len(n2.Conns()) != 1 || len(n3.Conns()) != 1 { |
|||
t.Errorf("should have (1,1) conn. Got: (%d, %d)", len(n2.Conns()), len(n3.Conns())) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// p := PrinterTo(os.Stdout)
|
|||
// p.NetworkConns(n1)
|
|||
// p.NetworkConns(n2)
|
|||
// p.NetworkConns(n3)
|
|||
|
|||
// can create a stream 2->3, 3->2,
|
|||
if _, err := n2.NewStream(p3); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if _, err := n3.NewStream(p2); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// but not 1->2 nor 2->2 (not linked), nor 1->1 (not connected)
|
|||
if _, err := n1.NewStream(p2); err == nil { |
|||
t.Error("should not be able to connect") |
|||
} |
|||
if _, err := n2.NewStream(p2); err == nil { |
|||
t.Error("should not be able to connect") |
|||
} |
|||
if _, err := n1.NewStream(p1); err == nil { |
|||
t.Error("should not be able to connect") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// connect p1->p1 (should work)
|
|||
if _, err := n1.DialPeer(ctx, p1); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error("p1 should be able to dial self.", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// and a stream too
|
|||
if _, err := n1.NewStream(p1); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// connect p1->p2
|
|||
if _, err := n1.DialPeer(ctx, p2); err == nil { |
|||
t.Error("p1 should not be able to dial p2, not connected...") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// connect p3->p1
|
|||
if _, err := n3.DialPeer(ctx, p1); err == nil { |
|||
t.Error("p3 should not be able to dial p1, not connected...") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// relink p1->p2
|
|||
|
|||
l12, err = mn.LinkPeers(p1, p2) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !(l12.Networks()[0] == n1 && l12.Networks()[1] == n2) && |
|||
!(l12.Networks()[0] == n2 && l12.Networks()[1] == n1) { |
|||
t.Error("l12 networks incorrect") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// should now be able to connect
|
|||
|
|||
// connect p1->p2
|
|||
if _, err := n1.DialPeer(ctx, p2); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// and a stream should work now too :)
|
|||
if _, err := n2.NewStream(p3); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestStreams(t *testing.T) { |
|||
|
|||
mn, err := FullMeshConnected(context.Background(), 3) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
handler := func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
b := make([]byte, 4) |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(s, b); err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(b, []byte("beep")) { |
|||
panic("bytes mismatch") |
|||
} |
|||
if _, err := s.Write([]byte("boop")); err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
hosts := mn.Hosts() |
|||
for _, h := range mn.Hosts() { |
|||
h.SetStreamHandler(protocol.TestingID, handler) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
s, err := hosts[0].NewStream(protocol.TestingID, hosts[1].ID()) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if _, err := s.Write([]byte("beep")); err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
b := make([]byte, 4) |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(s, b); err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(b, []byte("boop")) { |
|||
panic("bytes mismatch 2") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func makePinger(st string, n int) func(inet.Stream) { |
|||
return func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
go func() { |
|||
defer s.Close() |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ { |
|||
b := make([]byte, 4+len(st)) |
|||
if _, err := s.Write([]byte("ping" + st)); err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(s, b); err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(b, []byte("pong"+st)) { |
|||
panic("bytes mismatch") |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
}() |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func makePonger(st string) func(inet.Stream) { |
|||
return func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
go func() { |
|||
defer s.Close() |
|||
|
|||
for { |
|||
b := make([]byte, 4+len(st)) |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(s, b); err != nil { |
|||
if err == io.EOF { |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(b, []byte("ping"+st)) { |
|||
panic("bytes mismatch") |
|||
} |
|||
if _, err := s.Write([]byte("pong" + st)); err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
}() |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestStreamsStress(t *testing.T) { |
|||
|
|||
mn, err := FullMeshConnected(context.Background(), 100) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
hosts := mn.Hosts() |
|||
for _, h := range hosts { |
|||
ponger := makePonger(string(protocol.TestingID)) |
|||
h.SetStreamHandler(protocol.TestingID, ponger) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
var wg sync.WaitGroup |
|||
for i := 0; i < 1000; i++ { |
|||
wg.Add(1) |
|||
go func(i int) { |
|||
defer wg.Done() |
|||
from := rand.Intn(len(hosts)) |
|||
to := rand.Intn(len(hosts)) |
|||
s, err := hosts[from].NewStream(protocol.TestingID, hosts[to].ID()) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
log.Debugf("%d (%s) %d (%s)", from, hosts[from], to, hosts[to]) |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Infof("%d start pinging", i) |
|||
makePinger("pingpong", rand.Intn(100))(s) |
|||
log.Infof("%d done pinging", i) |
|||
}(i) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
wg.Wait() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestAdding(t *testing.T) { |
|||
|
|||
mn := New(context.Background()) |
|||
|
|||
peers := []peer.ID{} |
|||
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ { |
|||
sk, _, err := testutil.RandKeyPair(512) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
a := testutil.RandLocalTCPAddress() |
|||
h, err := mn.AddPeer(sk, a) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
peers = append(peers, h.ID()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
p1 := peers[0] |
|||
p2 := peers[1] |
|||
|
|||
// link them
|
|||
for _, p1 := range peers { |
|||
for _, p2 := range peers { |
|||
if _, err := mn.LinkPeers(p1, p2); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// set the new stream handler on p2
|
|||
h2 := mn.Host(p2) |
|||
if h2 == nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("no host for %s", p2) |
|||
} |
|||
h2.SetStreamHandler(protocol.TestingID, func(s inet.Stream) { |
|||
defer s.Close() |
|||
|
|||
b := make([]byte, 4) |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(s, b); err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if string(b) != "beep" { |
|||
panic("did not beep!") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if _, err := s.Write([]byte("boop")); err != nil { |
|||
panic(err) |
|||
} |
|||
}) |
|||
|
|||
// connect p1 to p2
|
|||
if _, err := mn.ConnectPeers(p1, p2); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// talk to p2
|
|||
h1 := mn.Host(p1) |
|||
if h1 == nil { |
|||
t.Fatalf("no network for %s", p1) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
s, err := h1.NewStream(protocol.TestingID, p2) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if _, err := s.Write([]byte("beep")); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
b := make([]byte, 4) |
|||
if _, err := io.ReadFull(s, b); err != nil { |
|||
t.Error(err) |
|||
} |
|||
if !bytes.Equal(b, []byte("boop")) { |
|||
t.Error("bytes mismatch 2") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,124 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package swarm |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
conn "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/conn" |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
manet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr-net" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// ListenAddresses returns a list of addresses at which this swarm listens.
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) ListenAddresses() []ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
listeners := s.swarm.Listeners() |
|||
addrs := make([]ma.Multiaddr, 0, len(listeners)) |
|||
for _, l := range listeners { |
|||
if l2, ok := l.NetListener().(conn.Listener); ok { |
|||
addrs = append(addrs, l2.Multiaddr()) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return addrs |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// InterfaceListenAddresses returns a list of addresses at which this swarm
|
|||
// listens. It expands "any interface" addresses (/ip4/0.0.0.0, /ip6/::) to
|
|||
// use the known local interfaces.
|
|||
func InterfaceListenAddresses(s *Swarm) ([]ma.Multiaddr, error) { |
|||
return resolveUnspecifiedAddresses(s.ListenAddresses()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// resolveUnspecifiedAddresses expands unspecified ip addresses (/ip4/0.0.0.0, /ip6/::) to
|
|||
// use the known local interfaces.
|
|||
func resolveUnspecifiedAddresses(unspecifiedAddrs []ma.Multiaddr) ([]ma.Multiaddr, error) { |
|||
var outputAddrs []ma.Multiaddr |
|||
|
|||
// todo optimize: only fetch these if we have a "any" addr.
|
|||
ifaceAddrs, err := interfaceAddresses() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for _, a := range unspecifiedAddrs { |
|||
|
|||
// split address into its components
|
|||
split := ma.Split(a) |
|||
|
|||
// if first component (ip) is not unspecified, use it as is.
|
|||
if !manet.IsIPUnspecified(split[0]) { |
|||
outputAddrs = append(outputAddrs, a) |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// unspecified? add one address per interface.
|
|||
for _, ia := range ifaceAddrs { |
|||
split[0] = ia |
|||
joined := ma.Join(split...) |
|||
outputAddrs = append(outputAddrs, joined) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Event(context.TODO(), "interfaceListenAddresses", func() eventlog.Loggable { |
|||
var addrs []string |
|||
for _, addr := range outputAddrs { |
|||
addrs = append(addrs, addr.String()) |
|||
} |
|||
return eventlog.Metadata{"addresses": addrs} |
|||
}()) |
|||
log.Debug("InterfaceListenAddresses:", outputAddrs) |
|||
return outputAddrs, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// interfaceAddresses returns a list of addresses associated with local machine
|
|||
func interfaceAddresses() ([]ma.Multiaddr, error) { |
|||
maddrs, err := manet.InterfaceMultiaddrs() |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
var nonLoopback []ma.Multiaddr |
|||
for _, a := range maddrs { |
|||
if !manet.IsIPLoopback(a) { |
|||
nonLoopback = append(nonLoopback, a) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return nonLoopback, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// addrInList returns whether or not an address is part of a list.
|
|||
// this is useful to check if NAT is happening (or other bugs?)
|
|||
func addrInList(addr ma.Multiaddr, list []ma.Multiaddr) bool { |
|||
for _, addr2 := range list { |
|||
if addr.Equal(addr2) { |
|||
return true |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return false |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// checkNATWarning checks if our observed addresses differ. if so,
|
|||
// informs the user that certain things might not work yet
|
|||
func checkNATWarning(s *Swarm, observed ma.Multiaddr, expected ma.Multiaddr) { |
|||
if observed.Equal(expected) { |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
listen, err := InterfaceListenAddresses(s) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
log.Errorf("Error retrieving swarm.InterfaceListenAddresses: %s", err) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if !addrInList(observed, listen) { // probably a nat
|
|||
log.Warningf(natWarning, observed, listen) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
const natWarning = `Remote peer observed our address to be: %s |
|||
The local addresses are: %s |
|||
Thus, connection is going through NAT, and other connections may fail. |
|||
|
|||
IPFS NAT traversal is still under development. Please bug us on github or irc to fix this. |
|||
Baby steps: http://jbenet.static.s3.amazonaws.com/271dfcf/baby-steps.gif
|
|||
` |
|||
@ -1,66 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package swarm |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"sync" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
func TestSimultOpen(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("skipping for another test")
|
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
swarms, peers := makeSwarms(ctx, t, 2) |
|||
|
|||
// connect everyone
|
|||
{ |
|||
var wg sync.WaitGroup |
|||
connect := func(s *Swarm, dst peer.ID, addr ma.Multiaddr) { |
|||
// copy for other peer
|
|||
s.peers.AddAddress(dst, addr) |
|||
if _, err := s.Dial(ctx, dst); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal("error swarm dialing to peer", err) |
|||
} |
|||
wg.Done() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Info("Connecting swarms simultaneously.") |
|||
wg.Add(2) |
|||
go connect(swarms[0], swarms[1].local, peers[1].Addr) |
|||
go connect(swarms[1], swarms[0].local, peers[0].Addr) |
|||
wg.Wait() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for _, s := range swarms { |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestSimultOpenMany(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("very very slow")
|
|||
|
|||
addrs := 20 |
|||
SubtestSwarm(t, addrs, 10) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestSimultOpenFewStress(t *testing.T) { |
|||
if testing.Short() { |
|||
t.SkipNow() |
|||
} |
|||
// t.Skip("skipping for another test")
|
|||
|
|||
msgs := 40 |
|||
swarms := 2 |
|||
rounds := 10 |
|||
// rounds := 100
|
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < rounds; i++ { |
|||
SubtestSwarm(t, swarms, msgs) |
|||
<-time.After(10 * time.Millisecond) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,158 +0,0 @@ |
|||
// package swarm implements a connection muxer with a pair of channels
|
|||
// to synchronize all network communication.
|
|||
package swarm |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
eventlog "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ctxgroup "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-ctxgroup" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
ps "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-peerstream" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
var log = eventlog.Logger("swarm2") |
|||
|
|||
// Swarm is a connection muxer, allowing connections to other peers to
|
|||
// be opened and closed, while still using the same Chan for all
|
|||
// communication. The Chan sends/receives Messages, which note the
|
|||
// destination or source Peer.
|
|||
//
|
|||
// Uses peerstream.Swarm
|
|||
type Swarm struct { |
|||
swarm *ps.Swarm |
|||
local peer.ID |
|||
peers peer.Peerstore |
|||
connh ConnHandler |
|||
|
|||
cg ctxgroup.ContextGroup |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NewSwarm constructs a Swarm, with a Chan.
|
|||
func NewSwarm(ctx context.Context, listenAddrs []ma.Multiaddr, |
|||
local peer.ID, peers peer.Peerstore) (*Swarm, error) { |
|||
|
|||
s := &Swarm{ |
|||
swarm: ps.NewSwarm(), |
|||
local: local, |
|||
peers: peers, |
|||
cg: ctxgroup.WithContext(ctx), |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// configure Swarm
|
|||
s.cg.SetTeardown(s.teardown) |
|||
s.SetConnHandler(nil) // make sure to setup our own conn handler.
|
|||
|
|||
return s, s.listen(listenAddrs) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) teardown() error { |
|||
return s.swarm.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// CtxGroup returns the Context Group of the swarm
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) CtxGroup() ctxgroup.ContextGroup { |
|||
return s.cg |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Close stops the Swarm.
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) Close() error { |
|||
return s.cg.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// StreamSwarm returns the underlying peerstream.Swarm
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) StreamSwarm() *ps.Swarm { |
|||
return s.swarm |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// SetConnHandler assigns the handler for new connections.
|
|||
// See peerstream. You will rarely use this. See SetStreamHandler
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) SetConnHandler(handler ConnHandler) { |
|||
|
|||
// handler is nil if user wants to clear the old handler.
|
|||
if handler == nil { |
|||
s.swarm.SetConnHandler(func(psconn *ps.Conn) { |
|||
s.connHandler(psconn) |
|||
}) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
s.swarm.SetConnHandler(func(psconn *ps.Conn) { |
|||
// sc is nil if closed in our handler.
|
|||
if sc := s.connHandler(psconn); sc != nil { |
|||
// call the user's handler. in a goroutine for sync safety.
|
|||
go handler(sc) |
|||
} |
|||
}) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// SetStreamHandler assigns the handler for new streams.
|
|||
// See peerstream.
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) SetStreamHandler(handler inet.StreamHandler) { |
|||
s.swarm.SetStreamHandler(func(s *ps.Stream) { |
|||
handler(wrapStream(s)) |
|||
}) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NewStreamWithPeer creates a new stream on any available connection to p
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) NewStreamWithPeer(p peer.ID) (*Stream, error) { |
|||
// if we have no connections, try connecting.
|
|||
if len(s.ConnectionsToPeer(p)) == 0 { |
|||
log.Debug("Swarm: NewStreamWithPeer no connections. Attempting to connect...") |
|||
if _, err := s.Dial(context.Background(), p); err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
log.Debug("Swarm: NewStreamWithPeer...") |
|||
|
|||
st, err := s.swarm.NewStreamWithGroup(p) |
|||
return wrapStream(st), err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// StreamsWithPeer returns all the live Streams to p
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) StreamsWithPeer(p peer.ID) []*Stream { |
|||
return wrapStreams(ps.StreamsWithGroup(p, s.swarm.Streams())) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ConnectionsToPeer returns all the live connections to p
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) ConnectionsToPeer(p peer.ID) []*Conn { |
|||
return wrapConns(ps.ConnsWithGroup(p, s.swarm.Conns())) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Connections returns a slice of all connections.
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) Connections() []*Conn { |
|||
return wrapConns(s.swarm.Conns()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// CloseConnection removes a given peer from swarm + closes the connection
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) CloseConnection(p peer.ID) error { |
|||
conns := s.swarm.ConnsWithGroup(p) // boom.
|
|||
for _, c := range conns { |
|||
c.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Peers returns a copy of the set of peers swarm is connected to.
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) Peers() []peer.ID { |
|||
conns := s.Connections() |
|||
|
|||
seen := make(map[peer.ID]struct{}) |
|||
peers := make([]peer.ID, 0, len(conns)) |
|||
for _, c := range conns { |
|||
p := c.RemotePeer() |
|||
if _, found := seen[p]; found { |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
peers = append(peers, p) |
|||
} |
|||
return peers |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer returns the local peer swarm is associated to.
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) LocalPeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return s.local |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,141 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package swarm |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
|
|||
ic "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/crypto" |
|||
conn "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/conn" |
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
ps "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-peerstream" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// a Conn is a simple wrapper around a ps.Conn that also exposes
|
|||
// some of the methods from the underlying conn.Conn.
|
|||
// There's **five** "layers" to each connection:
|
|||
// * 0. the net.Conn - underlying net.Conn (TCP/UDP/UTP/etc)
|
|||
// * 1. the manet.Conn - provides multiaddr friendly Conn
|
|||
// * 2. the conn.Conn - provides Peer friendly Conn (inc Secure channel)
|
|||
// * 3. the peerstream.Conn - provides peerstream / spdysptream happiness
|
|||
// * 4. the Conn - abstracts everyting out, exposing only key parts of underlying layers
|
|||
// (I know, this is kinda crazy. it's more historical than a good design. though the
|
|||
// layers do build up pieces of functionality. and they're all just io.RW :) )
|
|||
type Conn ps.Conn |
|||
|
|||
// ConnHandler is called when new conns are opened from remote peers.
|
|||
// See peerstream.ConnHandler
|
|||
type ConnHandler func(*Conn) |
|||
|
|||
func (c *Conn) StreamConn() *ps.Conn { |
|||
return (*ps.Conn)(c) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *Conn) RawConn() conn.Conn { |
|||
// righly panic if these things aren't true. it is an expected
|
|||
// invariant that these Conns are all of the typewe expect:
|
|||
// ps.Conn wrapping a conn.Conn
|
|||
// if we get something else it is programmer error.
|
|||
return (*ps.Conn)(c).NetConn().(conn.Conn) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *Conn) String() string { |
|||
return fmt.Sprintf("<SwarmConn %s>", c.RawConn()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalMultiaddr is the Multiaddr on this side
|
|||
func (c *Conn) LocalMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.RawConn().LocalMultiaddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPeer is the Peer on our side of the connection
|
|||
func (c *Conn) LocalPeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.RawConn().LocalPeer() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemoteMultiaddr is the Multiaddr on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *Conn) RemoteMultiaddr() ma.Multiaddr { |
|||
return c.RawConn().RemoteMultiaddr() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemotePeer is the Peer on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *Conn) RemotePeer() peer.ID { |
|||
return c.RawConn().RemotePeer() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// LocalPrivateKey is the public key of the peer on this side
|
|||
func (c *Conn) LocalPrivateKey() ic.PrivKey { |
|||
return c.RawConn().LocalPrivateKey() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// RemotePublicKey is the public key of the peer on the remote side
|
|||
func (c *Conn) RemotePublicKey() ic.PubKey { |
|||
return c.RawConn().RemotePublicKey() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NewSwarmStream returns a new Stream from this connection
|
|||
func (c *Conn) NewSwarmStream() (*Stream, error) { |
|||
s, err := c.StreamConn().NewStream() |
|||
return wrapStream(s), err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// NewStream returns a new Stream from this connection
|
|||
func (c *Conn) NewStream() (inet.Stream, error) { |
|||
s, err := c.NewSwarmStream() |
|||
return inet.Stream(s), err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func (c *Conn) Close() error { |
|||
return c.StreamConn().Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func wrapConn(psc *ps.Conn) (*Conn, error) { |
|||
// grab the underlying connection.
|
|||
if _, ok := psc.NetConn().(conn.Conn); !ok { |
|||
// this should never happen. if we see it ocurring it means that we added
|
|||
// a Listener to the ps.Swarm that is NOT one of our net/conn.Listener.
|
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("swarm connHandler: invalid conn (not a conn.Conn): %s", psc) |
|||
} |
|||
return (*Conn)(psc), nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// wrapConns returns a *Conn for all these ps.Conns
|
|||
func wrapConns(conns1 []*ps.Conn) []*Conn { |
|||
conns2 := make([]*Conn, len(conns1)) |
|||
for i, c1 := range conns1 { |
|||
if c2, err := wrapConn(c1); err == nil { |
|||
conns2[i] = c2 |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
return conns2 |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// newConnSetup does the swarm's "setup" for a connection. returns the underlying
|
|||
// conn.Conn this method is used by both swarm.Dial and ps.Swarm connHandler
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) newConnSetup(ctx context.Context, psConn *ps.Conn) (*Conn, error) { |
|||
|
|||
// wrap with a Conn
|
|||
sc, err := wrapConn(psConn) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// if we have a public key, make sure we add it to our peerstore!
|
|||
// This is an important detail. Otherwise we must fetch the public
|
|||
// key from the DHT or some other system.
|
|||
if pk := sc.RemotePublicKey(); pk != nil { |
|||
s.peers.AddPubKey(sc.RemotePeer(), pk) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok great! we can use it. add it to our group.
|
|||
|
|||
// set the RemotePeer as a group on the conn. this lets us group
|
|||
// connections in the StreamSwarm by peer, and get a streams from
|
|||
// any available connection in the group (better multiconn):
|
|||
// swarm.StreamSwarm().NewStreamWithGroup(remotePeer)
|
|||
psConn.AddGroup(sc.RemotePeer()) |
|||
|
|||
return sc, nil |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,104 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package swarm |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"errors" |
|||
"fmt" |
|||
|
|||
conn "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/conn" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
lgbl "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog/loggables" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// Dial connects to a peer.
|
|||
//
|
|||
// The idea is that the client of Swarm does not need to know what network
|
|||
// the connection will happen over. Swarm can use whichever it choses.
|
|||
// This allows us to use various transport protocols, do NAT traversal/relay,
|
|||
// etc. to achive connection.
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) Dial(ctx context.Context, p peer.ID) (*Conn, error) { |
|||
|
|||
if p == s.local { |
|||
return nil, errors.New("Attempted connection to self!") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// check if we already have an open connection first
|
|||
cs := s.ConnectionsToPeer(p) |
|||
for _, c := range cs { |
|||
if c != nil { // dump out the first one we find
|
|||
return c, nil |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
sk := s.peers.PrivKey(s.local) |
|||
if sk == nil { |
|||
// may be fine for sk to be nil, just log a warning.
|
|||
log.Warning("Dial not given PrivateKey, so WILL NOT SECURE conn.") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
remoteAddrs := s.peers.Addresses(p) |
|||
if len(remoteAddrs) == 0 { |
|||
return nil, errors.New("peer has no addresses") |
|||
} |
|||
localAddrs := s.peers.Addresses(s.local) |
|||
if len(localAddrs) == 0 { |
|||
log.Debug("Dialing out with no local addresses.") |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// open connection to peer
|
|||
d := &conn.Dialer{ |
|||
LocalPeer: s.local, |
|||
LocalAddrs: localAddrs, |
|||
PrivateKey: sk, |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// try to connect to one of the peer's known addresses.
|
|||
// for simplicity, we do this sequentially.
|
|||
// A future commit will do this asynchronously.
|
|||
var connC conn.Conn |
|||
var err error |
|||
for _, addr := range remoteAddrs { |
|||
connC, err = d.Dial(ctx, addr, p) |
|||
if err == nil { |
|||
break |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok try to setup the new connection.
|
|||
swarmC, err := dialConnSetup(ctx, s, connC) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
log.Error("Dial newConnSetup failed. disconnecting.") |
|||
log.Event(ctx, "dialFailureDisconnect", lgbl.NetConn(connC), lgbl.Error(err)) |
|||
swarmC.Close() // close the connection. didn't work out :(
|
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Event(ctx, "dial", p) |
|||
return swarmC, nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// dialConnSetup is the setup logic for a connection from the dial side. it
|
|||
// needs to add the Conn to the StreamSwarm, then run newConnSetup
|
|||
func dialConnSetup(ctx context.Context, s *Swarm, connC conn.Conn) (*Conn, error) { |
|||
|
|||
psC, err := s.swarm.AddConn(connC) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
// connC is closed by caller if we fail.
|
|||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to add conn to ps.Swarm: %s", err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// ok try to setup the new connection. (newConnSetup will add to group)
|
|||
swarmC, err := s.newConnSetup(ctx, psC) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
log.Error("Dial newConnSetup failed. disconnecting.") |
|||
log.Event(ctx, "dialFailureDisconnect", lgbl.NetConn(connC), lgbl.Error(err)) |
|||
swarmC.Close() // we need to call this to make sure psC is Closed.
|
|||
return nil, err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return swarmC, err |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,86 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package swarm |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
conn "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net/conn" |
|||
lgbl "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/eventlog/loggables" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
ps "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-peerstream" |
|||
multierr "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/multierr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// Open listeners for each network the swarm should listen on
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) listen(addrs []ma.Multiaddr) error { |
|||
retErr := multierr.New() |
|||
|
|||
// listen on every address
|
|||
for i, addr := range addrs { |
|||
err := s.setupListener(addr) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
if retErr.Errors == nil { |
|||
retErr.Errors = make([]error, len(addrs)) |
|||
} |
|||
retErr.Errors[i] = err |
|||
log.Errorf("Failed to listen on: %s - %s", addr, err) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if retErr.Errors != nil { |
|||
return retErr |
|||
} |
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Listen for new connections on the given multiaddr
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) setupListener(maddr ma.Multiaddr) error { |
|||
|
|||
// TODO rethink how this has to work. (jbenet)
|
|||
//
|
|||
// resolved, err := resolveUnspecifiedAddresses([]ma.Multiaddr{maddr})
|
|||
// if err != nil {
|
|||
// return err
|
|||
// }
|
|||
// for _, a := range resolved {
|
|||
// s.peers.AddAddress(s.local, a)
|
|||
// }
|
|||
|
|||
sk := s.peers.PrivKey(s.local) |
|||
if sk == nil { |
|||
// may be fine for sk to be nil, just log a warning.
|
|||
log.Warning("Listener not given PrivateKey, so WILL NOT SECURE conns.") |
|||
} |
|||
list, err := conn.Listen(s.cg.Context(), maddr, s.local, sk) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// AddListener to the peerstream Listener. this will begin accepting connections
|
|||
// and streams!
|
|||
_, err = s.swarm.AddListener(list) |
|||
return err |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// connHandler is called by the StreamSwarm whenever a new connection is added
|
|||
// here we configure it slightly. Note that this is sequential, so if anything
|
|||
// will take a while do it in a goroutine.
|
|||
// See https://godoc.org/github.com/jbenet/go-peerstream for more information
|
|||
func (s *Swarm) connHandler(c *ps.Conn) *Conn { |
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
// this context is for running the handshake, which -- when receiveing connections
|
|||
// -- we have no bound on beyond what the transport protocol bounds it at.
|
|||
// note that setup + the handshake are bounded by underlying io.
|
|||
// (i.e. if TCP or UDP disconnects (or the swarm closes), we're done.
|
|||
// Q: why not have a shorter handshake? think about an HTTP server on really slow conns.
|
|||
// as long as the conn is live (TCP says its online), it tries its best. we follow suit.)
|
|||
|
|||
sc, err := s.newConnSetup(ctx, c) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
log.Error(err) |
|||
log.Event(ctx, "newConnHandlerDisconnect", lgbl.NetConn(c.NetConn()), lgbl.Error(err)) |
|||
c.Close() // boom. close it.
|
|||
return nil |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return sc |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,59 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package swarm |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
|
|||
ps "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-peerstream" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
// a Stream is a wrapper around a ps.Stream that exposes a way to get
|
|||
// our Conn and Swarm (instead of just the ps.Conn and ps.Swarm)
|
|||
type Stream ps.Stream |
|||
|
|||
// Stream returns the underlying peerstream.Stream
|
|||
func (s *Stream) Stream() *ps.Stream { |
|||
return (*ps.Stream)(s) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Conn returns the Conn associated with this Stream, as an inet.Conn
|
|||
func (s *Stream) Conn() inet.Conn { |
|||
return s.SwarmConn() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// SwarmConn returns the Conn associated with this Stream, as a *Conn
|
|||
func (s *Stream) SwarmConn() *Conn { |
|||
return (*Conn)(s.Stream().Conn()) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Wait waits for the stream to receive a reply.
|
|||
func (s *Stream) Wait() error { |
|||
return s.Stream().Wait() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Read reads bytes from a stream.
|
|||
func (s *Stream) Read(p []byte) (n int, err error) { |
|||
return s.Stream().Read(p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Write writes bytes to a stream, flushing for each call.
|
|||
func (s *Stream) Write(p []byte) (n int, err error) { |
|||
return s.Stream().Write(p) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Close closes the stream, indicating this side is finished
|
|||
// with the stream.
|
|||
func (s *Stream) Close() error { |
|||
return s.Stream().Close() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func wrapStream(pss *ps.Stream) *Stream { |
|||
return (*Stream)(pss) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func wrapStreams(st []*ps.Stream) []*Stream { |
|||
out := make([]*Stream, len(st)) |
|||
for i, s := range st { |
|||
out[i] = wrapStream(s) |
|||
} |
|||
return out |
|||
} |
|||
@ -1,269 +0,0 @@ |
|||
package swarm |
|||
|
|||
import ( |
|||
"bytes" |
|||
"io" |
|||
"sync" |
|||
"testing" |
|||
"time" |
|||
|
|||
inet "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/net2" |
|||
peer "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/p2p/peer" |
|||
errors "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/debugerror" |
|||
testutil "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/util/testutil" |
|||
|
|||
context "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/code.google.com/p/go.net/context" |
|||
ma "github.com/jbenet/go-ipfs/Godeps/_workspace/src/github.com/jbenet/go-multiaddr" |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
func EchoStreamHandler(stream inet.Stream) { |
|||
go func() { |
|||
defer stream.Close() |
|||
|
|||
// pull out the ipfs conn
|
|||
c := stream.Conn() |
|||
log.Debugf("%s ponging to %s", c.LocalPeer(), c.RemotePeer()) |
|||
|
|||
buf := make([]byte, 4) |
|||
|
|||
for { |
|||
if _, err := stream.Read(buf); err != nil { |
|||
if err != io.EOF { |
|||
log.Error("ping receive error:", err) |
|||
} |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if !bytes.Equal(buf, []byte("ping")) { |
|||
log.Errorf("ping receive error: ping != %s %v", buf, buf) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if _, err := stream.Write([]byte("pong")); err != nil { |
|||
log.Error("pond send error:", err) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
}() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func makeSwarms(ctx context.Context, t *testing.T, num int) ([]*Swarm, []testutil.PeerNetParams) { |
|||
swarms := make([]*Swarm, 0, num) |
|||
peersnp := make([]testutil.PeerNetParams, 0, num) |
|||
|
|||
for i := 0; i < num; i++ { |
|||
localnp := testutil.RandPeerNetParamsOrFatal(t) |
|||
peersnp = append(peersnp, localnp) |
|||
|
|||
peerstore := peer.NewPeerstore() |
|||
peerstore.AddAddress(localnp.ID, localnp.Addr) |
|||
peerstore.AddPubKey(localnp.ID, localnp.PubKey) |
|||
peerstore.AddPrivKey(localnp.ID, localnp.PrivKey) |
|||
|
|||
addrs := peerstore.Addresses(localnp.ID) |
|||
swarm, err := NewSwarm(ctx, addrs, localnp.ID, peerstore) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
swarm.SetStreamHandler(EchoStreamHandler) |
|||
swarms = append(swarms, swarm) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
return swarms, peersnp |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func connectSwarms(t *testing.T, ctx context.Context, swarms []*Swarm, peersnp []testutil.PeerNetParams) { |
|||
|
|||
var wg sync.WaitGroup |
|||
connect := func(s *Swarm, dst peer.ID, addr ma.Multiaddr) { |
|||
// TODO: make a DialAddr func.
|
|||
s.peers.AddAddress(dst, addr) |
|||
if _, err := s.Dial(ctx, dst); err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal("error swarm dialing to peer", err) |
|||
} |
|||
wg.Done() |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Info("Connecting swarms simultaneously.") |
|||
for _, s := range swarms { |
|||
for _, p := range peersnp { |
|||
if p.ID != s.local { // don't connect to self.
|
|||
wg.Add(1) |
|||
connect(s, p.ID, p.Addr) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
wg.Wait() |
|||
|
|||
for _, s := range swarms { |
|||
log.Infof("%s swarm routing table: %s", s.local, s.Peers()) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func SubtestSwarm(t *testing.T, SwarmNum int, MsgNum int) { |
|||
// t.Skip("skipping for another test")
|
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
swarms, peersnp := makeSwarms(ctx, t, SwarmNum) |
|||
|
|||
// connect everyone
|
|||
connectSwarms(t, ctx, swarms, peersnp) |
|||
|
|||
// ping/pong
|
|||
for _, s1 := range swarms { |
|||
log.Debugf("-------------------------------------------------------") |
|||
log.Debugf("%s ping pong round", s1.local) |
|||
log.Debugf("-------------------------------------------------------") |
|||
|
|||
_, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx) |
|||
got := map[peer.ID]int{} |
|||
errChan := make(chan error, MsgNum*len(peersnp)) |
|||
streamChan := make(chan *Stream, MsgNum) |
|||
|
|||
// send out "ping" x MsgNum to every peer
|
|||
go func() { |
|||
defer close(streamChan) |
|||
|
|||
var wg sync.WaitGroup |
|||
send := func(p peer.ID) { |
|||
defer wg.Done() |
|||
|
|||
// first, one stream per peer (nice)
|
|||
stream, err := s1.NewStreamWithPeer(p) |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
errChan <- errors.Wrap(err) |
|||
return |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// send out ping!
|
|||
for k := 0; k < MsgNum; k++ { // with k messages
|
|||
msg := "ping" |
|||
log.Debugf("%s %s %s (%d)", s1.local, msg, p, k) |
|||
stream.Write([]byte(msg)) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// read it later
|
|||
streamChan <- stream |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for _, p := range peersnp { |
|||
if p.ID == s1.local { |
|||
continue // dont send to self...
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
wg.Add(1) |
|||
go send(p.ID) |
|||
} |
|||
wg.Wait() |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
// receive "pong" x MsgNum from every peer
|
|||
go func() { |
|||
defer close(errChan) |
|||
count := 0 |
|||
countShouldBe := MsgNum * (len(peersnp) - 1) |
|||
for stream := range streamChan { // one per peer
|
|||
defer stream.Close() |
|||
|
|||
// get peer on the other side
|
|||
p := stream.Conn().RemotePeer() |
|||
|
|||
// receive pings
|
|||
msgCount := 0 |
|||
msg := make([]byte, 4) |
|||
for k := 0; k < MsgNum; k++ { // with k messages
|
|||
|
|||
// read from the stream
|
|||
if _, err := stream.Read(msg); err != nil { |
|||
errChan <- errors.Wrap(err) |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if string(msg) != "pong" { |
|||
errChan <- errors.Errorf("unexpected message: %s", msg) |
|||
continue |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s %s %s (%d)", s1.local, msg, p, k) |
|||
msgCount++ |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
got[p] = msgCount |
|||
count += msgCount |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
if count != countShouldBe { |
|||
errChan <- errors.Errorf("count mismatch: %d != %d", count, countShouldBe) |
|||
} |
|||
}() |
|||
|
|||
// check any errors (blocks till consumer is done)
|
|||
for err := range errChan { |
|||
if err != nil { |
|||
t.Fatal(err.Error()) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
log.Debugf("%s got pongs", s1.local) |
|||
if (len(peersnp) - 1) != len(got) { |
|||
t.Errorf("got (%d) less messages than sent (%d).", len(got), len(peersnp)) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for p, n := range got { |
|||
if n != MsgNum { |
|||
t.Error("peer did not get all msgs", p, n, "/", MsgNum) |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
cancel() |
|||
<-time.After(10 * time.Millisecond) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
for _, s := range swarms { |
|||
s.Close() |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestSwarm(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("skipping for another test")
|
|||
|
|||
// msgs := 1000
|
|||
msgs := 100 |
|||
swarms := 5 |
|||
SubtestSwarm(t, swarms, msgs) |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
func TestConnHandler(t *testing.T) { |
|||
// t.Skip("skipping for another test")
|
|||
|
|||
ctx := context.Background() |
|||
swarms, peersnp := makeSwarms(ctx, t, 5) |
|||
|
|||
gotconn := make(chan struct{}, 10) |
|||
swarms[0].SetConnHandler(func(conn *Conn) { |
|||
gotconn <- struct{}{} |
|||
}) |
|||
|
|||
connectSwarms(t, ctx, swarms, peersnp) |
|||
|
|||
<-time.After(time.Millisecond) |
|||
// should've gotten 5 by now.
|
|||
|
|||
swarms[0].SetConnHandler(nil) |
|||
|
|||
expect := 4 |
|||
for i := 0; i < expect; i++ { |
|||
select { |
|||
case <-time.After(time.Second): |
|||
t.Fatal("failed to get connections") |
|||
case <-gotconn: |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
select { |
|||
case <-gotconn: |
|||
t.Fatalf("should have connected to %d swarms", expect) |
|||
default: |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
Loading…
Reference in new issue